Figure 1.
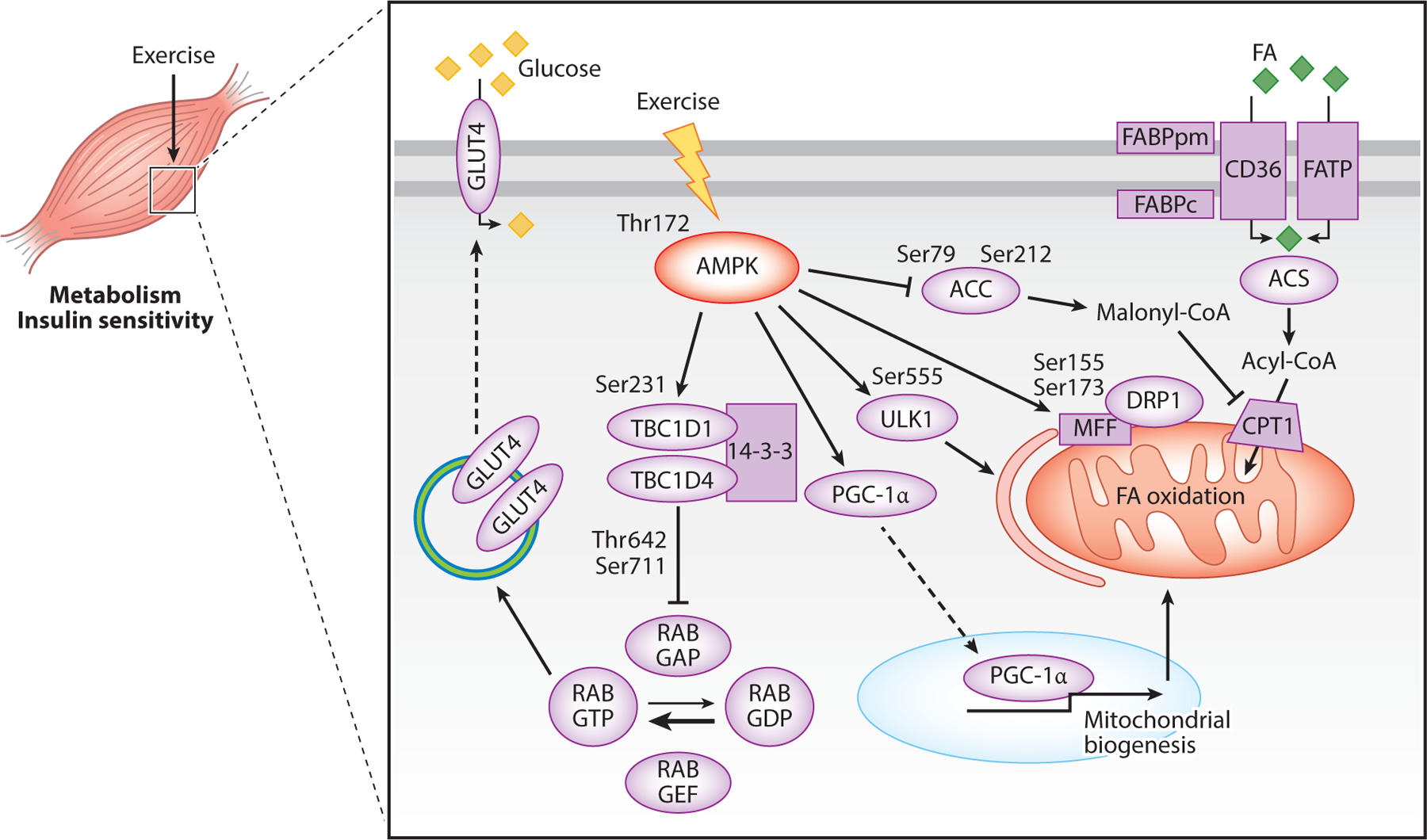
Mechanisms by which exercise-induced AMPK modifies metabolism in skeletal muscle. Phosphorylation of AMPK at Thr172 increases glucose uptake by phosphorylating TBC1D1 and TBC1D4, thus promoting their binding to 14-3-3, which inhibits RAB GAP activity. This leads to increased RAB GTP, which promotes mobilization of GLUT4 to the membrane. AMPK activation also increases FA oxidation. FAs are taken up into the cell by a group of FA transport proteins; FAs are then converted to acyl-CoA and taken into the mitochondria by CPT1 for oxidation. AMPK activation promotes FA uptake by phosphorylating and inhibiting ACC. This inhibits ACC synthesis of malonyl-CoA and prevents malonyl-CoA from inhibiting CTP1, thus promoting FA uptake into the mitochondria and FA oxidation. Lastly, AMPK activation promotes PGC-1α activity, resulting in translocation of PGC-1α to the nucleus, where it functions to promote transcription of mitochondrial genes. Abbreviations: ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ACS, acyl-CoA synthetase; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; CD36, fatty acid translocase; CPT1, carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1; DRP1, dynamin-related protein 1; FA, fatty acid; FABPc, fatty acid–binding protein cytosolic; FABPpm, fatty acid–binding protein plasma membrane; FATP, fatty acid transport protein; GLUT4, glucose transporter type 4; MFF, mitochondrial fission factor; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 alpha; RAB GAP, GTPase-activating protein–bound form of RAB; RAB GDP, guanosine diphosphate–bound form of RAB; RAB GEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factor–bound form of RAB; RAB GTP, guanosine-5′-triphosphate-bound form of RAB; Ser, serine; TBC1D1, TBC1 domain family member 1; TBC1D4, TBC1 domain family member 4; Thr, threonine; ULK1, Unc-51-like autophagy activating kinase 1.
