Figure 2.
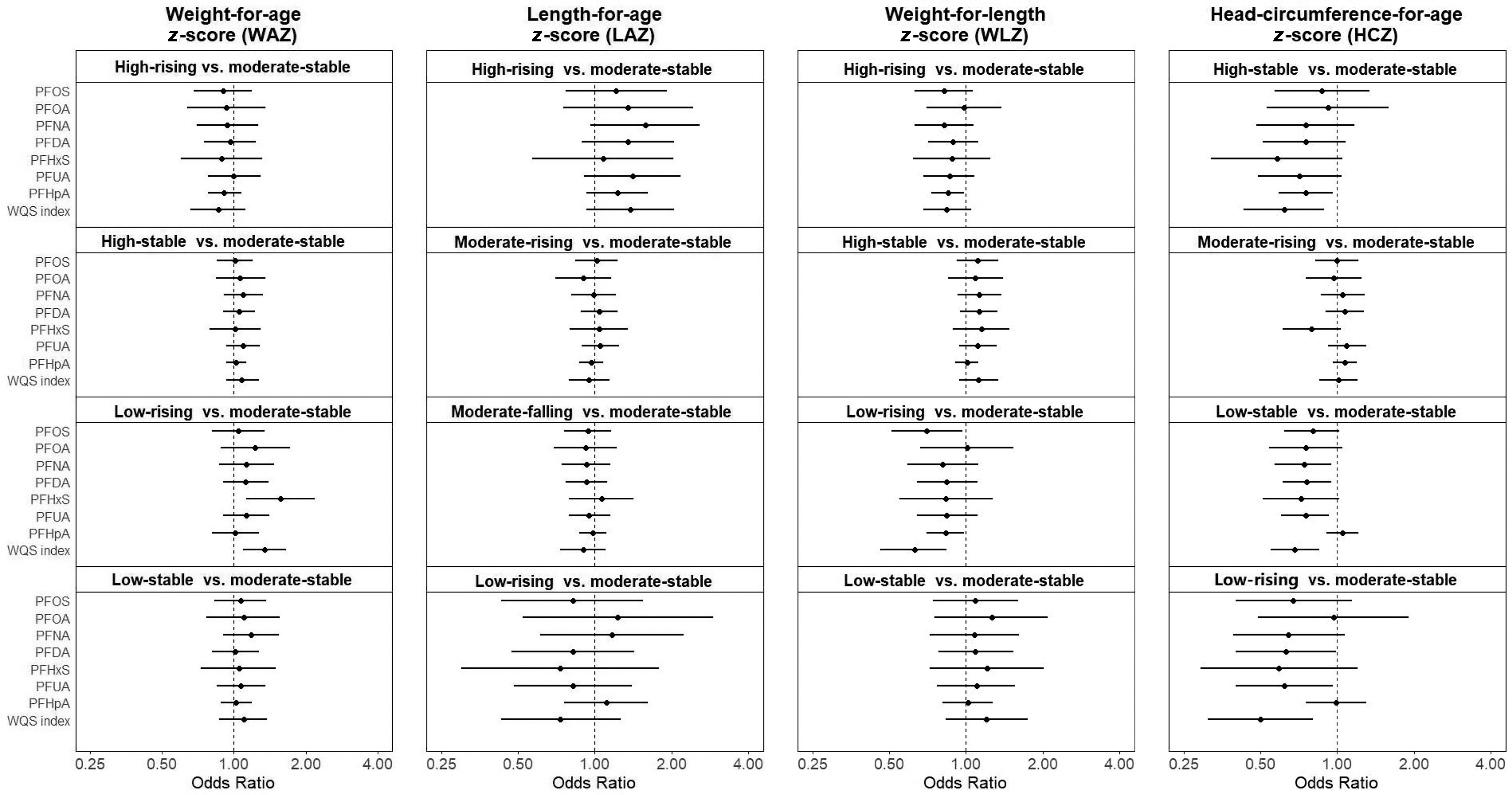
OR and 95% CI for trajectory groups in each anthropometrical measure according to per doubling increase in prenatal PFAS level (nanograms per milliliter) in logistic regression models in Shanghai Birth Cohort, Shanghai, China, recruited from 2013 to 2016. A WQS index was created using all seven types of PFAS to reflect the mixture exposure level. All models were adjusted for maternal age, maternal education, prepregnancy BMI, fish and seafood intake during pregnancy, parity, and pregnancy eGFR. Numeric values are presented in Table S6. Note: BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HCZ, head-circumference-for-age z-score; for LAZ, length-for-age z-score; PFAS, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances; PFDA, perfluorodecanoic acid; PFHpA, perfluoroheptanoic acid; PFHxS, perfluorohexanesulfonic acid; PFNA, perfluorononanoic acid; PFOA, perfluorooctanoic acid; PFOS, perfluorooctane sulfonic acid; PFUA, perfluoroundecanoic acid; OR, odds ratio; WAZ, weight-for-age z-score; WLZ, weight-for-length z-score; WQS, weighted quantile sum.
