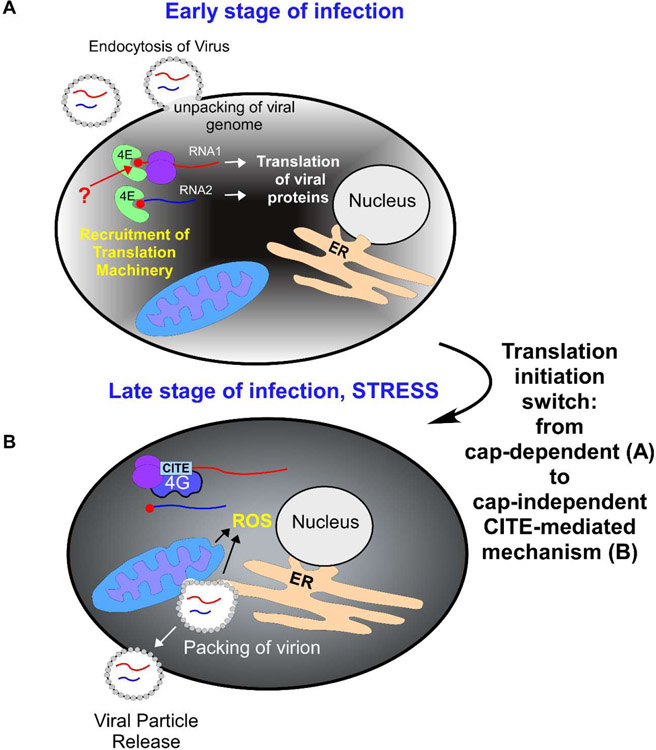
Figure 2: Translation initiation switch model for black beetle virus RNA1 5′-UTR CITE.
During early stages of infection (A), both black beetle virus (BBV) RNAs (RNA1 is shown in red, RNA2 is shown in blue) are translated via canonical cap-dependent translation initiation mechanism, in which the RNA1 5′-UTR CITE element functions as a Kozak sequence to enhance start codon selection. In later stages of BBV infection (B), cap-dependent translation is downregulated due to stress induced, in part, by disruption of mitochondrial and ER membranes for virion packaging and accompanying release of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Under these conditions, BBV RNA1 5′-UTR CITE activity is switched to operate in cap-independent translation initiation.