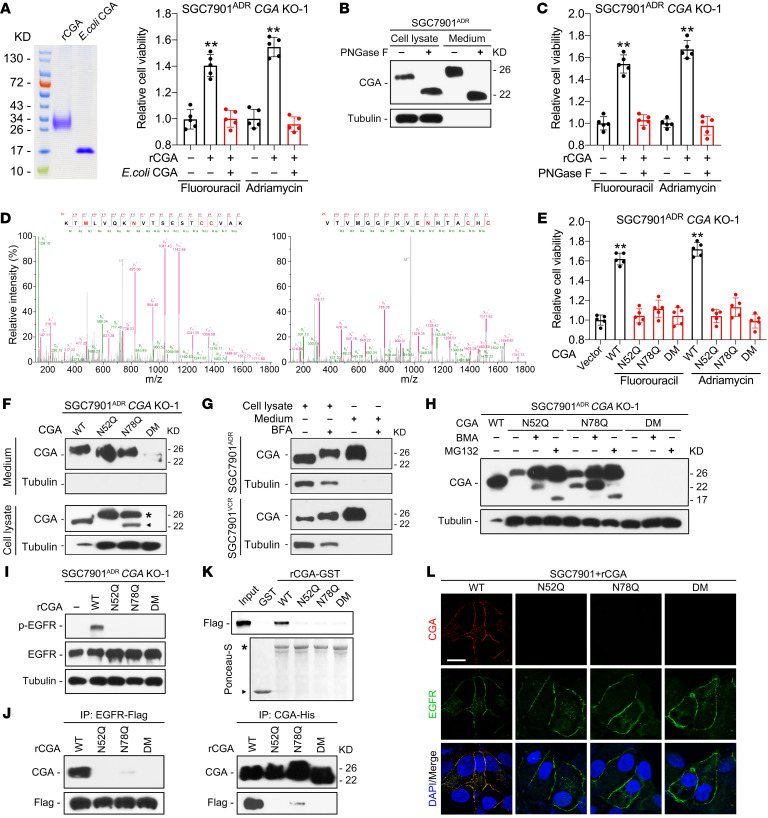
Figure 4. N-glycosylation is required for CGA-induced chemoresistance.
(A) Left: SDS-PAGE of purified CGA from HEK293FT cells (rCGA) and E. coli (E. coli CGA). Right: Viability of CGA–/– SGC7901ADR cells treated with rCGA or E. coli CGA and chemotherapy. (B and C) Immunoblotting of lysate and conditioned medium from PNGase F–treated SGC7901ADR cells (B), with viability measured in indicated cells treated with chemotherapy (C). (D) MS/MS spectra of CGA secreted by SGC7901ADR cells shows 2 N-glycosylation sites, Asn52 (left) and Asn78 (right), in CGA. N in red indicates the glycosylation sites. (E) Viability of CGA–/– SGC7901ADR cells transfected with WT, N52Q, N78Q, or N52Q/N78Q double mutant (DM) CGA and treated with chemotherapy. (F) Immunoblotting of lysates and conditioned medium CGA from CGA–/– SGC7901ADR cells transfected with WT, N52Q, N78Q, or DM CGA. Asterisk and arrowhead indicate CGA band shifts. (G) Immunoblotting of lysate and conditioned medium CGA from MDR cells treated with BFA (5 nM). (H) Immunoblotting of CGA from CGA–/– SGC7901ADR cells transfected with WT, N52Q, N78Q, or DM CGA and treated with BMA (1 μM) or MG132 (10 μM). (I) Immunoblotting of p-EGFR and EGFR in CGA–/– SGC7901ADR cells treated with purified WT, N52Q, N78Q, or DM rCGA. (J) Immunoblotting of lysates from SGC7901 cells transfected with Flag-tagged EGFR were incubated with purified His-tagged CGA after immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag and anti-His antibodies. (K) Top: Immunoblotting for Flag of bound proteins after GST or GST fusion proteins were incubated with equal amounts of lysates from Flag-tagged EGFR-ECD–expressing HEK293T cells. Bottom: Ponceau-S staining to detect bait proteins. Arrowhead and asterisk indicate GST and GST fusion proteins, respectively. (L) IF staining of CGA, EGFR, and DAPI staining in SGC7901 cells treated with WT, N52Q, N78Q, or DM rCGA for 10 minutes at 4°C. Scale bar: 10 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01 by 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test (A, C, and E).