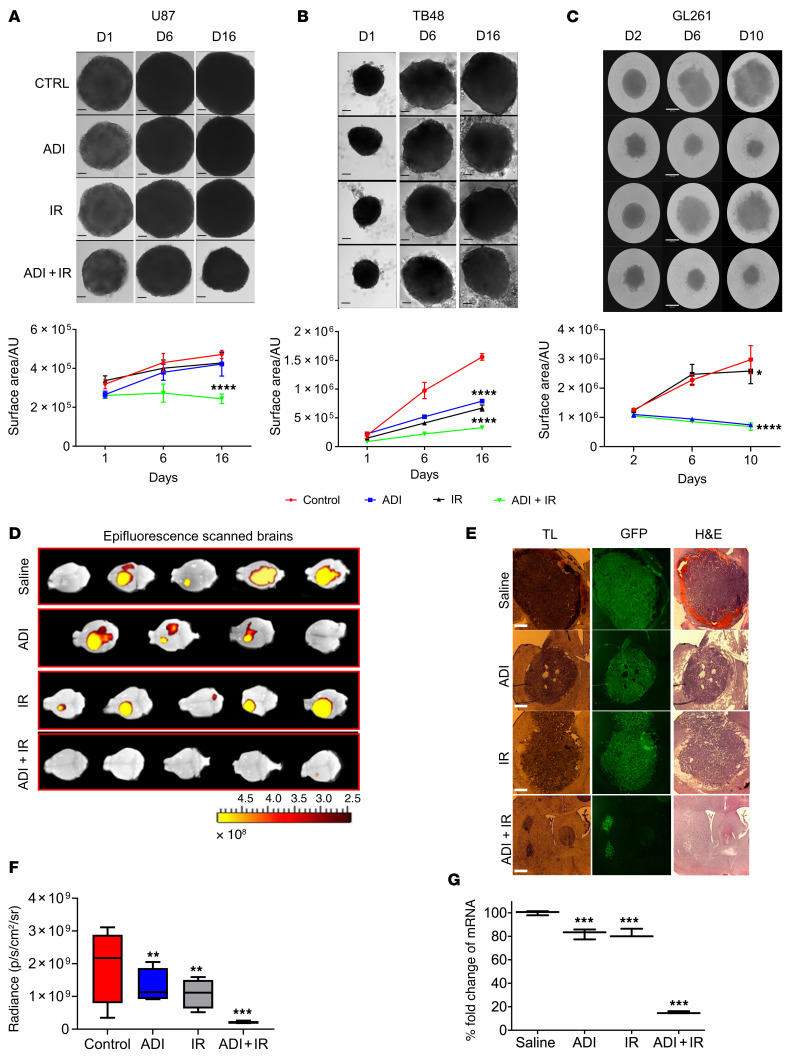
Figure 1. ADI-PEG20 in combination with radiation significantly reduces the growth of ASS1-positive GBM neurospheres and inhibits tumor growth in syngeneic mice.
Five thousand cells were plated in low-attachment 96-well plates and incubated for 3 to 8 days to allow formation of neurospheres. Neurospheres were pretreated with ADI-PEG20 (1 μg/mL for human lines and 0.25 μg/mL for mouse line, GL261) for 24 hours before exposure to 2 Gy of ionizing radiation (IR). (A–C) Images were taken on indicated days after IR treatment and changes in neurosphere surface area measured using ImageJ software (upper and lower panels). (D) Epifluorescence (GFP intensity) was measured in whole brains using in vivo image analysis (IVIS). (E) Microscopic analysis of representative brain sections: transmitted light (TL), GFP, and H&E staining. Scale bars: 360 μm (A–C) and 430 μm (E). (F) Tumor size is represented as total radiant efficiency. (G) qPCR expression levels of GFP in tumor sections. The neurosphere results are presented as mean ± SD, n = 12. The in vivo results were obtained from 5 animals per group except for animals treated with ADI-PEG20 monotherapy, which only had 4 animals due to the premature death of 1 mouse. Data were analyzed using 1-way ANOVA (A–C and F) or 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test with adjusted P values reported (G). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. AU, arbitrary units.