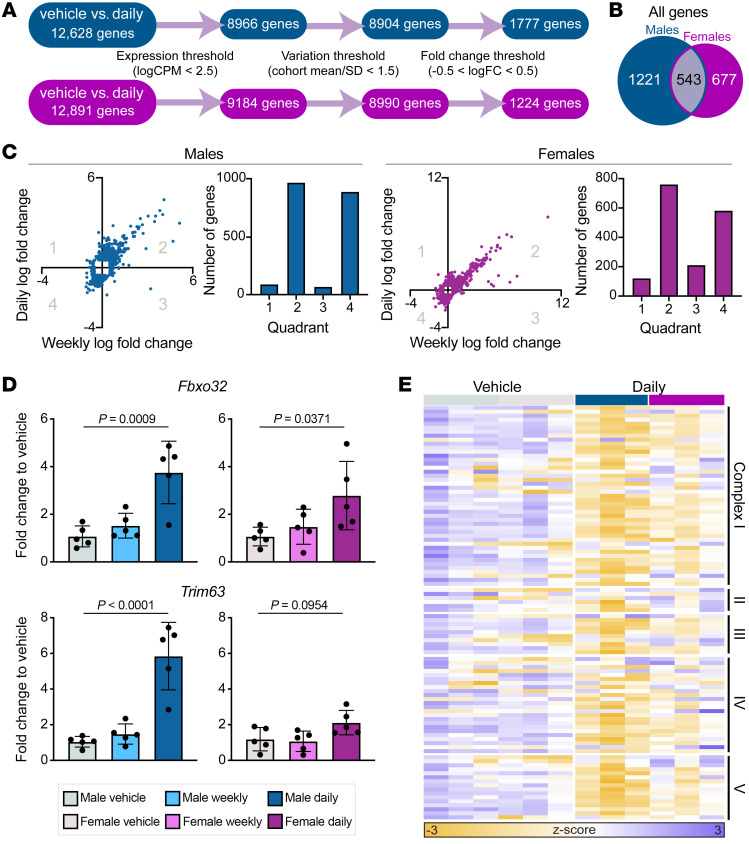
Figure 2. Daily and weekly prednisone treatment elicited similar transcriptional profiles with differential atrogene activation.
(A) RNA sequencing analysis of daily prednisone–treated muscles (quadriceps) compared with vehicle-treated for both sexes; prednisone-responsive genes were identified as being above expression and fold-change thresholds and below a variation threshold; n = 3 animals per group. (B) Less than half of all prednisone-responsive genes were shared among daily prednisone–treated males and females. (C) The majority of prednisone-responsive genes above a log2(fold change) threshold had the same response to both daily and weekly treatment, i.e., increased (quadrant 2) or decreased (quadrant 4) expression. (D) Expression of atrogenes Fbxo32 and Trim63 was increased in daily treated muscle fibers compared with vehicle, as evaluated by qPCR and 1-way ANOVA, while weekly treated muscle fibers had no change in expression of these atrogenes. (E) Expression of genes encoding the mitochondrial respiratory chain was decreased in response to daily treatment in both sexes compared with vehicle treatment.