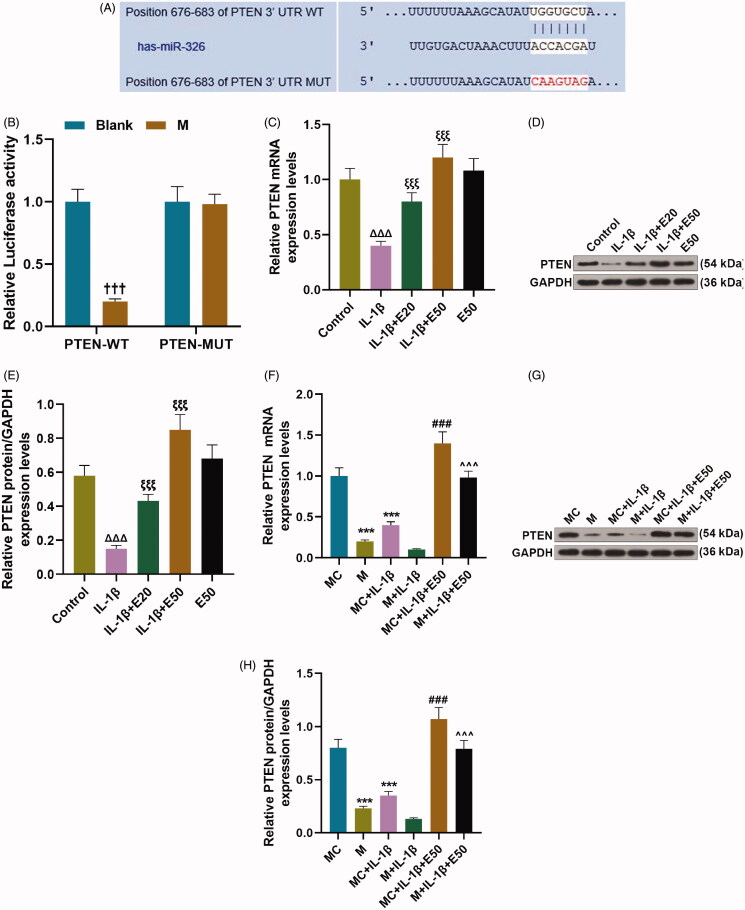
Figure 3.
EGCG indirectly increased phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) expression via decreasing miR-29b-3p in IL-1β-stimulated CHON-001 cells. (A, B) The binding relationship between miR-29b-3p and PTEN was predicted by TargetScan V7.2 (A) and verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay (B). (C–E) CHON-001 cells were divided into control, IL-1β, IL-1β + E20, IL-1β + E50 and E50 groups. The protein (C, D) and mRNA (E) levels of PTEN in CHON-001 cells were determined by qRT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. (F–H) CHON-001 cells were divided into MC, M, MC + IL-1β, M + IL-1β, MC + IL-1β + E50 and M + IL-1β + E50 groups. The protein (F, G) and mRNA (H) levels of PTEN in CHON-001 cells were determined by qRT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. GAPDH was used as the internal reference control for PTEN. EGCG: epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate; E50: 50 μM EGCG; MC: mimics control; M: miR-29b-3p mimics; qRT-PCR: real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; control: CHON-001 cells cultured without IL-1β or EGCG. †††p < 0.001 vs. blank; ΔΔΔp < 0.001 vs. control; ξξξp < 0.001 vs. IL-1β; **p < 0.01 or ***p < 0.001 vs. MC; ∧∧∧p < 0.001 vs. M + IL-1β. All measurements were performed at least three times. Data were presented as the means ± standard deviation (SD).