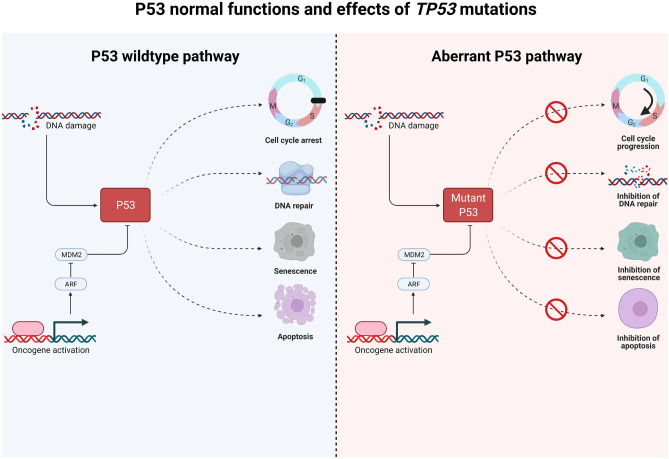
Fig. 39.
P53 normal functions and effects of TP53 mutations. In the wild-type state, P53 is activated upon DNA damage and inhibited via oncogene activation. P53 has many important cellular roles, including the regulation of cell cycle progression, DNA repair as well as regulation of cellular senescence and apoptosis. When inactivated by mutations or deletions, DNA damage accumulate, and cell cycle progression and inhibition of apoptosis is seen. Created with BioRender.com