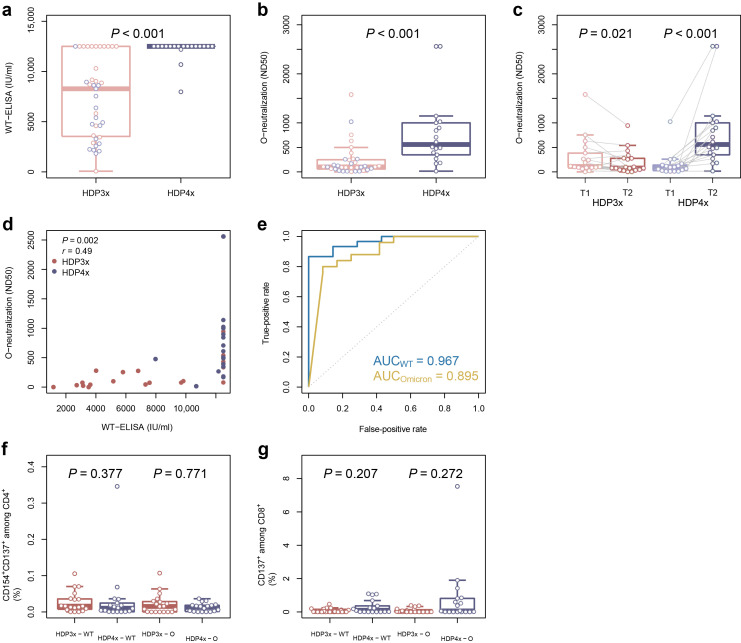
Figure 1.
Comparison of humoral and cellular immunity of hemodialysis patients vaccinated with 3 (HDP3x) or 4 (HDP4x) severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccine doses. Isolated serum samples from hemodialysis patients, vaccinated with 3 doses (n = 40) or 4 doses (n = 19), were analyzed for (a) titers (IU/ml) of binding antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 wild-type (WT) glycoprotein S and (b) omicron-specific neutralizing antibodies (ND50). (c) Comparison of omicron-specific neutralizing antibodies (ND50) after the third doses (T1, respectively), after 12 weeks (HDP3x, T2), or after the fourth doses (HDP4x, T2). Correlation between titers of SARS-CoV-2 WT binding and omicron-specific neutralizing antibodies (d) and receiver operating characteristic curve (e) for the predictive capacity of binding antibody titers against WT glycoprotein S for strong (>100 ND50) WT-specific (blue) and omicron-specific (yellow) neutralizing response, including the value for the area under the curve (AUC). (f,g) Isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from hemodialysis patients, vaccinated with 3 doses (HDP3x; n = 19) or 4 doses (HDP4x; n = 18), were stimulated for 16 hours with 1 μg/ml SARS-CoV-2 overlapping peptide pool from WT (left box plots) or the mutated regions of SARS-CoV-2 omicron lineage (O; right box plots). SARS-CoV-2–reactive T helper cells were identified as life/dead-marker–CD3+CD4+CD137+CD154+ (f), and SARS-CoV-2–reactive cytotoxic T cells were identified as life/dead-marker–CD3+CD8+CD137+ (g). In all box plots, red corresponds to the patients who received only 3 doses and blue to those who received all 4 doses; light colors refer to the time point after the third dose, whereas dark colors denote the time point after the fourth dose or 12 weeks after the third. Groups were compared using 2-sided, unpaired Mann-Whitney U-test, except for (c), where Wilcoxon signed-rank paired test was employed; the correlation (d) was evaluated employing the Pearson correlation coefficient. P ≤ 0.050 was defined as significant. ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.