Figure 4. Features of proteins with mitotic phosphorylation-dependent changes in cysteine reactivity.
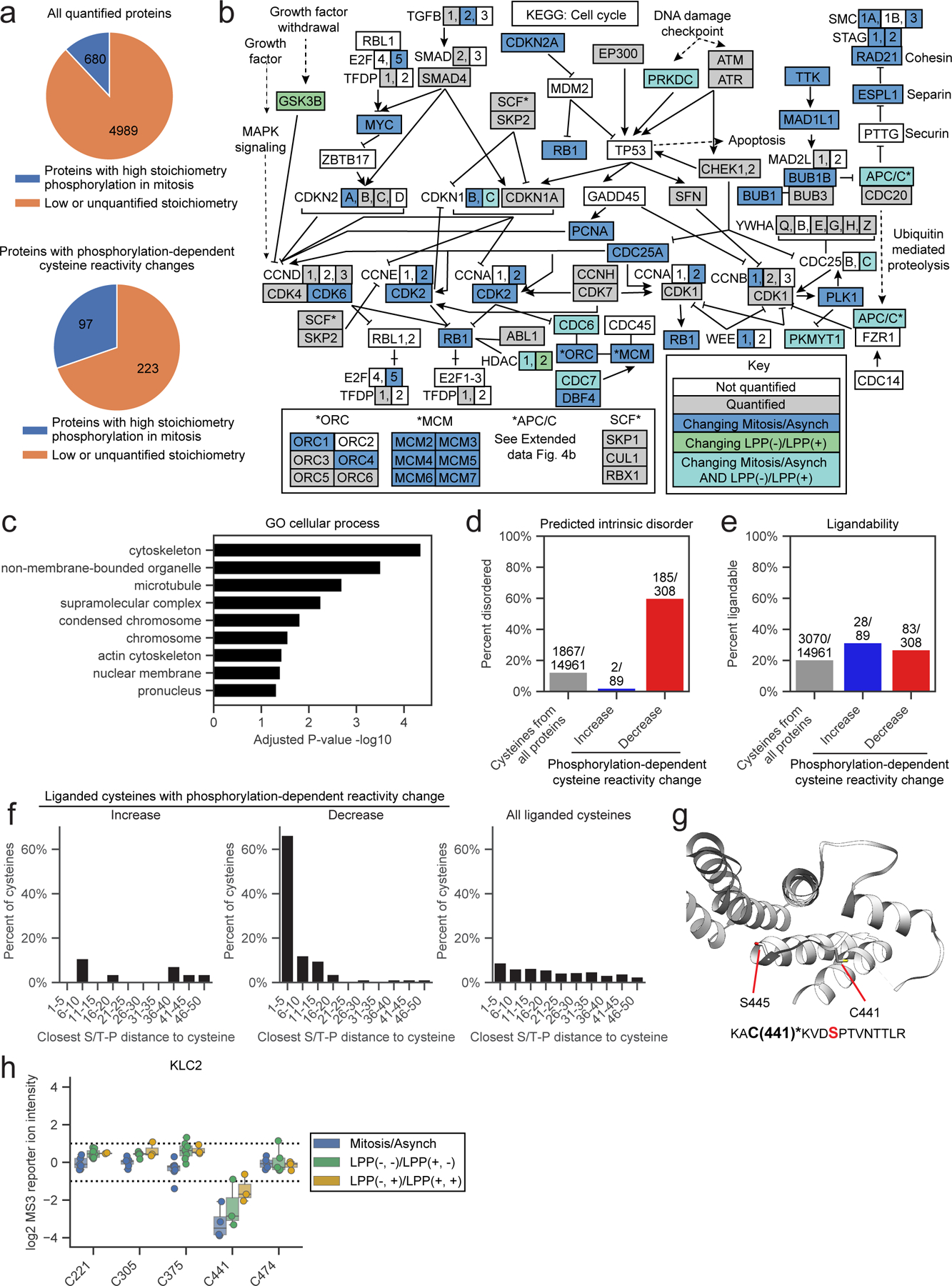
a, Proteins with phosphorylation-dependent cysteine reactivity changes (bottom) are enriched for high stoichiometry mitotic phosphorylation sites21 (> 50% occupancy; blue) compared to all quantified proteins (top). Proteins that only contained artifactual phosphorylation-dependent cysteine reactivity changes were excluded from the bottom pie chart. Proteins lacking sufficient data for phosphorylation stoichiometry calculation or exhibiting low stoichiometry (< 50% occupancy) sites in phosphoproteomics datasets21 were grouped and labeled as ‘Low or unquantified stoichiometry’ (orange). b, KEGG cell cycle pathway (HSA04110) diagram55 marking proteins with i) cell state- and phosphorylation-dependent cysteine reactivity changes in light blue; ii) only cell state-dependent cysteine reactivity changes in dark blue, iii) only phosphorylation-dependent cysteine reactivity changes, and iv) unchanging cysteine reactivities in gray. Proteins not quantified in our proteomic experiments are in white. c, GO cellular enrichment analysis of proteins with cell state- and phosphorylation-dependent cysteine reactivity changes.45, 46 Proteins with only artifactual phosphorylation-dependent cysteine reactivity changes were omitted from analysis. d, Percentage of cysteines from the indicated categories that reside in predicted disordered domains (IUPreD score > 0.5) based on IUPreD2A analysis.48 e, Percentage of cysteines from the indicated categories that are liganded by cysteine-reactive electrophilic small molecules; >80% engagement, as determined in references.39, 40, 42 f, Fraction of ligandable cysteines from the indicated categories showing phosphorylation-dependent reactivity changes within the specified amino acid distances from an S/T-P site. For d-f, artifactual phosphorylation-dependent cysteine reactivity changes were omitted from analysis. g, X-ray crystal structure of KLC2 (PDB: 3EDT)57 with the phosphorylation-dependent cysteine reactivity change – C441 – and the proximal serine in an S/T-P site – S445 – highlighted. Bottom, tryptic peptide from KLC2 containing C441 (asterisks, bold) and S445 (red, bold). h, Box plot showing cysteine reactivity values across indicated comparison groups for quantified cysteines in KLC2. Horizontal black line for each cysteine marks median value, boxes mark the upper and lower quartiles, and whiskers mark 1.5x interquartile range for n = 2 (or more) independent experiments (circles). Dotted lines designate boundaries for ≥ two-fold changes.
