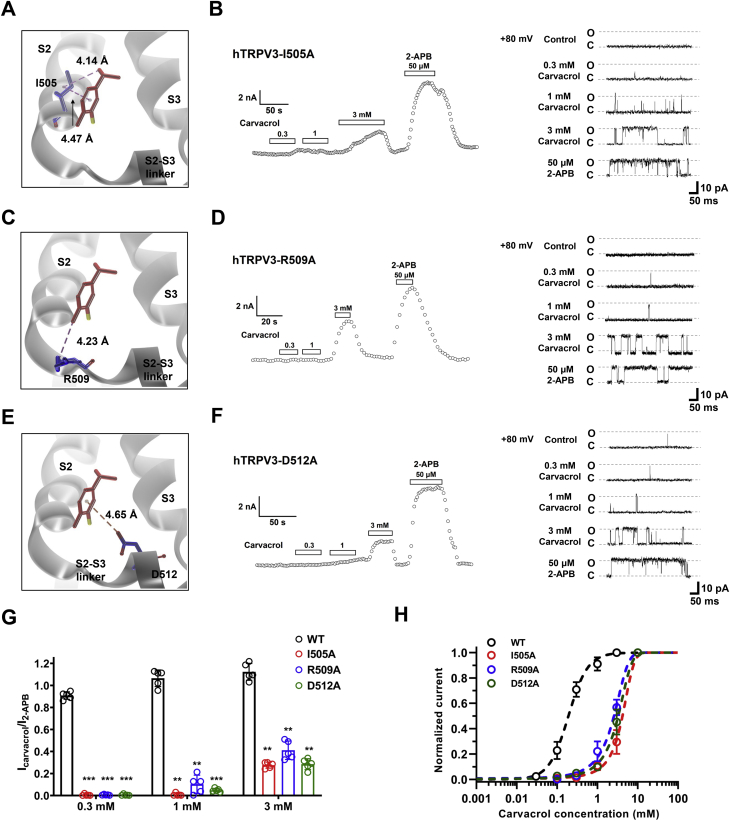
Figure 5.
Molecular determinants in the binding pocket of S2-S3 critical for activation of TRPV3 by carvacrol.A, molecular docking showing alkyl–alkyl & π–alkyl interactions between isopropyl arms and aromatic core of carvacrol and residue I505. B, representative whole-cell current recordings of TRPV3-I505A (left panel) and single-channel current traces (right panel) in response to different concentrations (0.3–3.0 mM) of carvacrol or 50 μM 2-APB (n = 5). C, molecular docking showing alkyl–alkyl interaction between methyl tail of carvacrol and residue R509. D, representative whole-cell current recordings of TRPV3-R509A (left panel) and single-channel current traces (right panel) in response to different concentrations (0.3–3.0 mM) of carvacrol or 50 μM 2-APB (n = 5). E, molecular docking showing π–anion interaction between carvacrol and residue D512. F, representative whole-cell current recordings of TRPV3-D512A (left panel) and single-channel current traces (right panel) in response to different concentrations (0.3–3.0 mM) of carvacrol or 50 μM 2-APB (n = 5). G, a summary of normalized currents for concentration-dependent activation of WT TRPV3 and mutant channels by carvacrol (0.3–3 mM) (n = 5). H, a summary for the comparison of concentration–response curves of activation of WT and mutant TRPV3 currents by carvacrol (n = 5). Dotted lines are fits to Hill equation, yielding WT TRPV3 with EC50 of 0.18 ± 0.03 mM (n = 5). Mutations I505A, R509A, and D512A showed EC50 values with 3.51 ± 0.44 mM, 2.93 ± 0.11 mM, and 3.21 ± 0.48 mM, respectively (n = 5). All data are expressed as the mean ± SD, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, by unpaired t test. 2-APB, 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate; TRPV3, Transient receptor potential vanilloid 3.