Figure 1.
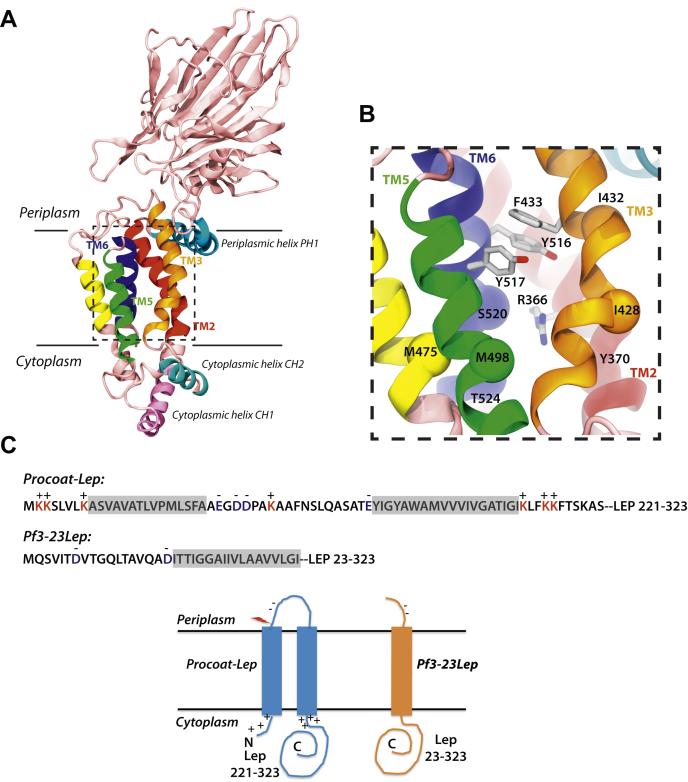
Structure of the Escherichia coli YidC and domain architecture of substrates.A, structure of the Escherichia coli YidC depicting its transmembrane and cytoplasmic helices. B, a closeup view of the hydrophilic groove (PDB 3WVF) (25). Residues studied in this paper are indicated, including the conserved positively charged R366, as well as the tyrosines and groove residues. Side chains are shown as stick for R366 and the aromatic residues mutated to study the requirement of the conserved arginine, while Cα atoms are shown as spheres for groove residues studied in Cys-alkylation assay. C, YidC substrates PC-Lep and Pf3-23Lep used in this study (see Experimental procedures for details) and their membrane topologies. The redarrow in PC-Lep depicts the cleavage site for signal peptidase. PC, procoat.