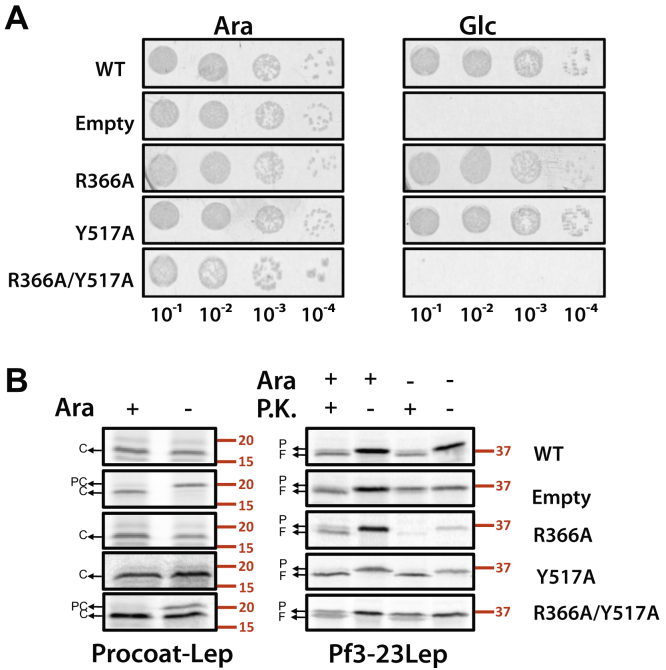
Figure 2.
The conserved R366 residue in Escherichia coli YidC becomes essential in the presence of the Y517A mutation.A, complementation assay to test the effect of mutating R366 and Y517 on Escherichia coli YidC function. pACYC184 encoding R366A, Y517A, and R366A/Y517A YidC mutants were constructed using site-directed mutagenesis and transformed into YidC depletion strain JS7131. After the depletion of endogenous YidC for 3 h, serial dilutions of the cells were spotted and incubated under YidC expression conditions (left panels) and depletion conditions (right panels), respectively (37 °C). Plasmid encoding WT YidC and empty plasmid were also expressed, as positive and negative controls. B, same E. coli YidC mutants were tested for their ability to insert PC-Lep (left panel) and Pf3-23Lep (right panel). JS7131 harboring pACYC184 encoding WT YidC, empty plasmid, or YidC mutants were cotransformed with pMS119 encoding PC-Lep or Pf3-23Lep. The cells were grown under YidC expression conditions (ara+) or depletion conditions (ara−) for 4 h (37 °C). Expression of the substrates was induced by 1 mM IPTG for 5 min and labeled with [35S]-methionine for 1 min. Signal peptide processing assay was used to assess the insertion of PC-Lep (left panel), and the insertion of Pf3-23Lep was examined by protease mapping (right panel), both as described in “Experimental procedures”. Red numbers indicate molecular weight marker values in kDa. C, Coat-Lep; PC, Procoat-Lep.