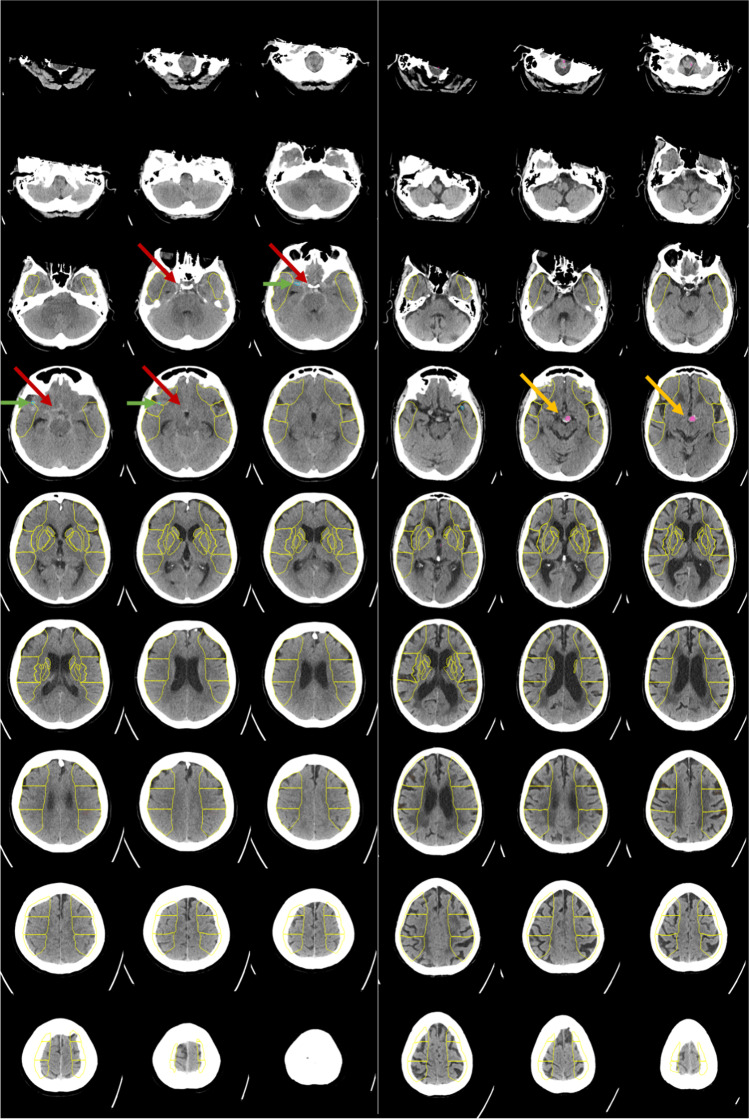
Fig. 5.
Two examples for patients with acute stroke symptoms for whom the detection of bleeding suspect hyperdense volumes was rated false negative (left) and false positive (right) by the Brainomix algorithm. In the false-negative case, an acute subarachnoid hemorrhage in the basal cisterns (red arrows) was not detected reliably by the algorithm; instead, a hyperdense vessel was marked (green arrows). In the false-positive case, an aneurysm of the basilar artery was detected wrongly as an intracranial bleeding suspect hyperdensity (yellow arrows)