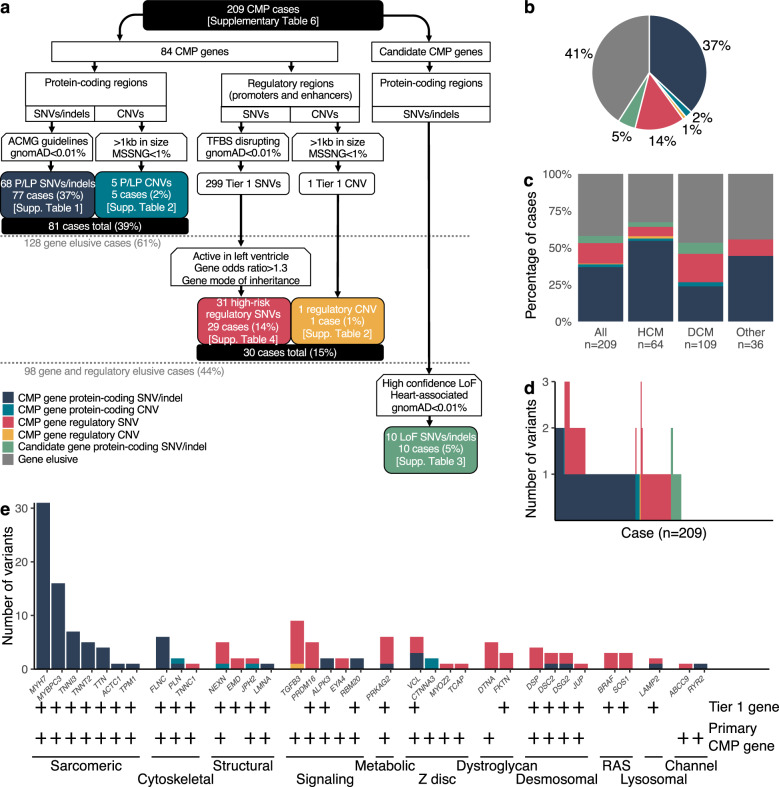
Fig. 1. Yield of protein-coding and regulatory variants in 209 unrelated childhood CMP cases.
a Flow-chart showing the selection process and yield of protein-coding and regulatory variants in the overall cohort and in the gene-elusive subset. Totally, 39% of all cases harbored at least one pathogenic protein-coding variant in a CMP gene; among the remaining 128 gene elusive cases, 15% harbored at least one prioritized high-risk regulatory variant in a CMP gene; and an additional 5% harbored an LoF variant in a new candidate CMP gene. b Pie diagram showing the distribution of protein-coding and regulatory variants in CMP genes and LoF variants in new CMP genes across the cohort (n = 209). WGS identified putatively pathogenic protein-coding SNVs/indels/CNVs in CMP genes in 39% of cases, high-risk variants in regulatory elements of CMP genes in an additional 15% of cases, and loss of function (LoF) variants in candidate genes in an additional 5% of cases. c Variant distribution by CMP subtypes: HCM cases had a higher yield of pathogenic protein-coding variants compared to other CMP subtypes (odds ratio 2.8, CI: 1.5–5.2, p = 7.07 × 10−4). d Variant burden by the patient: 9 cases (4.3%) had multiple protein-coding variants in known CMP genes, 2 cases (1.0%) had multiple prioritized regulatory variants, and 21 cases (10.0%) had both protein-coding and regulatory variants in CMP genes. Regulatory variants in all cases were further prioritized if they were active in human LV, were rare in control subpopulations (Popmax AF < 0.1%), and were associated with genes enriched in cases versus controls with OR ≥ 1.3. e Variant distribution by functional gene categories: of all the pathogenic protein-coding variants, 66% was in sarcomere genes which represented a significant enrichment compared to other gene categories (binomial p = 3.99 × 10−29). Conversely, none of the high-risk regulatory variants were in sarcomere genes. Tier 1 gene and primary CMP gene classifications are denoted by plus symbols. CMP cardiomyopathy, SNV single nucleotide variant, CNV copy number variant, gnomAD Genome Aggregation Database, ACMG American College of Medical Genetics; Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP), TFBS transcription factor binding site, P/LP pathogenic or likely pathogenic, LoF loss of function, HCM hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, DCM dilated cardiomyopathy.