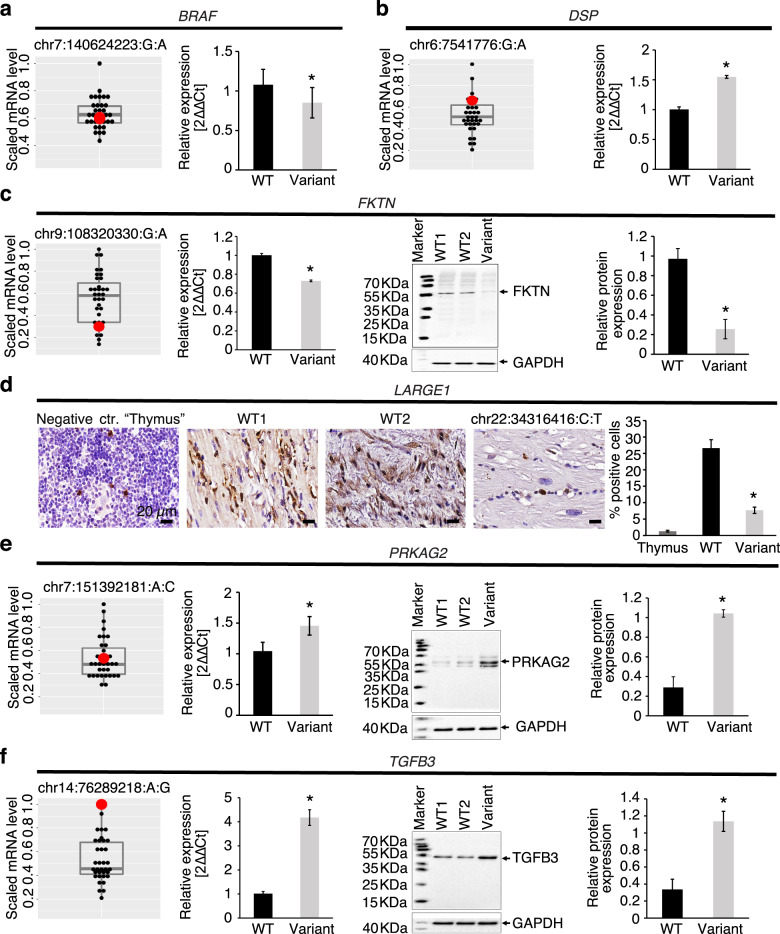
Fig. 4. Target gene and protein expression in the LV myocardium of patients harboring regulatory variants.
RNA Seq, qRT-PCR, Western blot, and immunohistochemistry were performed in available LV myocardium from CMP patients (n = 35) to detect mRNA and protein expression of target genes in patients harboring regulatory variants in BRAF, DSP, FKTN, LARGE1, PRKAG2, or TGFB3. For RNA sequencing data, the target scaled RPKM gene expression was compared between the patient harboring the variant (red dot) and the remainder of the cohort (black dots) using boxplots showing median expression for the cohort, 25th and 75th percentiles, and maximum and minimum values (n = 35). For qRT-PCR, Western blot, and immunohistochemistry, target gene or protein expression in the LV myocardium of the patient harboring the variant was compared to wild-type controls including an autopsy sample from an individual without cardiac disease as well as one or more CMP patients that did not harbor any known pathogenic coding or regulatory variants. Three independent experiments were performed per sample with each experiment including three technical replicates per sample. Protein expression level of GAPDH as a house keeping gene was used as a loading control for Western blots. Error bars indicate standard deviation between the averages of each independent experiment. a BRAF: Promoter variant chr7:140624223_G/A was associated with normal BRAF mRNA expression on RNAseq, but reduced BRAF mRNA expression on qRT-PCR. Promoter variant chr7:140624286_C/T was associated with increased mRNA expression on RNAseq (>75th percentile). b DSP: Promoter variant (chr6:7541776_G/A) was associated with increased DSP mRNA expression on RNAseq (>75th percentile), and on qRT-PCR (*p < 0.05 vs. controls). c FKTN: Promoter variant 1 (chr9:108320330_G/A) was associated with reduced FKTN mRNA expression on RNAseq (<75th percentile), reduced mRNA expression on qRT-PCR (p < 0.05 vs. controls), reduced protein expression on Western blot representative images, and reduced relative protein abundance on quantification (*p < 0.05 vs. controls). d LARGE1: Promoter variant chr22:34316416_C/T was associated with lower perinuclear staining for LARGE1 (brown) (nuclear staining, blue) on representative immunohistochemistry images, and lower % of LARGE1 positive cells in patient myocardium (*p < 0.05 vs. controls). Thymic tissue was used as a negative control. Scale bar = 20 µm. e PRKAG2: Enhancer variant chr7:151392181_A/C was associated with normal PRKAG2 mRNA expression on RNAseq, but higher mRNA expression on qRT-PCR (*p < 0.05 vs. controls), higher protein expression on Western blot representative images, and higher relative protein expression on quantification (*p < 0.05 vs. controls). f TGFB3: Enhancer variant (chr14:76289218_A/G) was associated with higher TGFB3 mRNA expression on RNAseq, higher mRNA expression on qRT-PCR (*p < 0.05 vs. controls), higher protein expression on Western blot representative images, and higher relative protein abundance on quantification (*p < 0.05 vs. controls). RNA Seq RNA sequencing, WT wild-type, 2ΔΔCt the relative fold-change in mRNA abundance between samples as a function of polymerase chain reaction thresholds.