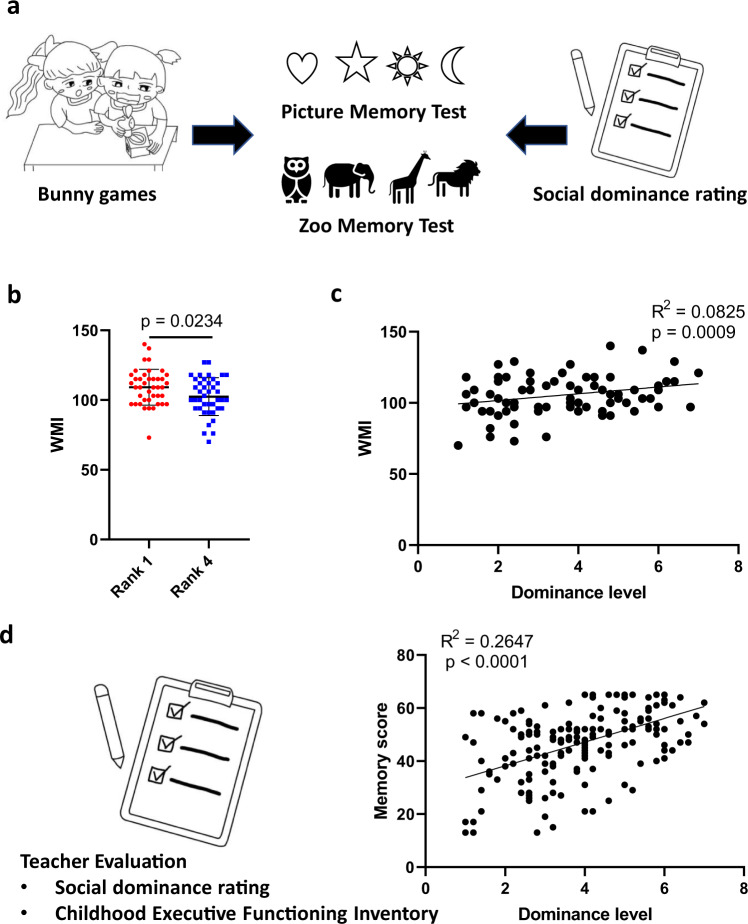
Fig. 5. Children with a higher rank or dominance levels showed better memory ability.
a Social ranks were defined by bunny games. The dominance levels were evaluated by social-dominance rating. The working-memory index (WMI) was evaluated and integrated by picture-memory and zoo-memory tests. The image is adapted from Chou et al. (2021)32. b The WMI for 1st- and 4th-rank children (unpaired t-test, n = 82). c The correlation between the WMI and dominance levels (Pearson correlation, n = 82). d The correlation between memory score evaluated by the Childhood Executive Functioning Inventory and dominance level evaluated by social-dominance rating (Pearson correlation, n = 175). Error bars = SEM.