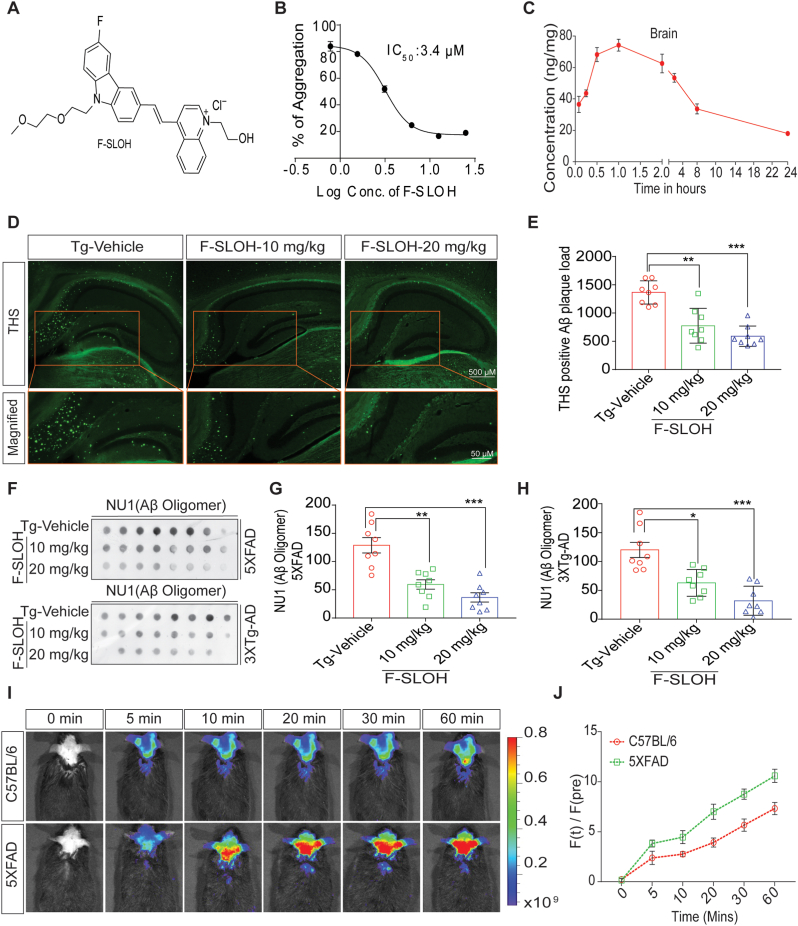
Fig. 1.
F-SLOH binds to Aβ species, inhibits Aβ fibrillation in vitro and reduces Aβ monomers, oligomers and plaques in preclinical AD animal models. (A) Chemical structure of F-SLOH. (B) F-SLOH dose-dependently inhibited the fibril formation of Aβ in the ThT anti-Aβ fibrillation fluorescence assay. The IC50 value of anti-fibrillation activity of F-SLOH is 3.4 μm. (C) Pharmacokinetic properties of F-SLOH. Concentration vs time after intraperitoneal administration at a dose of 20 mg/kg/d in brain tissue of ICR mice (N = 4). (D) F-SLOH treatment mitigates ThS-positive Aβ plaques in 5XFAD brain slice. F-SLOH (10 and 20 mg/kg) treatment reduces the ThS-positive plaques in 5XFAD mice when compared to Tg-vehicle and (E) its corresponding quantification. (F) Levels of NU1 (Aβ oligomer) presented in the dot blot representing treatment effects of F-SLOH (10 and 20 mg/kg) and its corresponding quantification of Aβ oligomers found in the brain lysates of (G) 5XFAD and (H) 3XTg-AD mice. Quantified data presented as mean ± SEM. N = 8. (I) Intra-peritoneal (IP) injection of F-SLOH (20 mg/kg) in 5XFAD mice and WT mice were observed using in vivo imaging in small animal imaging system (J) and its corresponding quantification.