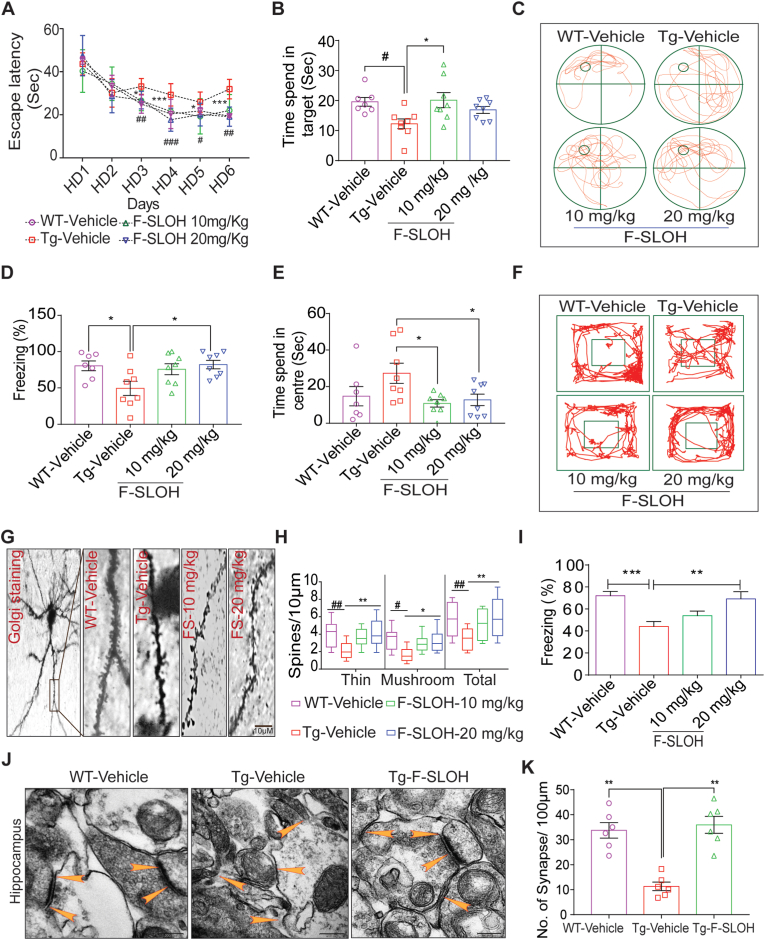
Fig. 3.
F-SLOH treatment improves spatial learning, memory function and augments synapse formation in AD mouse models. (A) F-SLOH-treated 3XTg-AD mice improved the spatial escape rate and decreased the escape latency during the learning period of six days in Morris water maze test when compared to the Tg-Vehicle group (N = 8). (B) F-SLOH-treated mice probed the platform placed quadrant for longer time when compared to the vehicle-treated Tg mice in the probe trial. (C) The images illustrate the animal's behaviour on the probe trial using video tracking software. (D) F-SLOH improves hippocampal-dependent memory and memory in F-SLOH-treated 3XTg-AD mice in comparison to the vehicle-treated Tg mice using contextual fear conditioning. (E) F-SLOH treatment improved exploratory behaviour and locomotor activity in open field experiment when compared to the Tg-Vehicle and its corresponding quantification. (F) Images illustrating the animal's locomotor behaviour in open field experiment using video tracking software. (G) Golgi staining of brain hippocampal slice from the F-SLOH-treated 3XTg-AD mice and Tg vehicle. (H) Data show an increase in thin and mushroom structures of spines along with total length of the spines when compared between the Tg-vehicle group and F-SLOH treatment (10 and 20 mg/kg) groups in a dose-dependent manner, indicating improved spinogenesis. (I) F-SLOH improved hippocampal-dependent memory in F-SLOH-treated 5XFAD mice when compared to the vehicle-treated Tg mice using contextual fear conditioning. (J) F-SLOH treatment ameliorates hippocampal-dependent synapse formation in the brain slices of 5XFAD mice. The ultrastructure of the synapse displayed in electron micrograph indicates that F-SLOH treatment improved the synapse formation in comparison to the vehicle-treated Tg group. (K) Quantification of number of synapses in the brain slice of 5XFAD mice. Quantified data presented as mean ± SEM. N = 8.