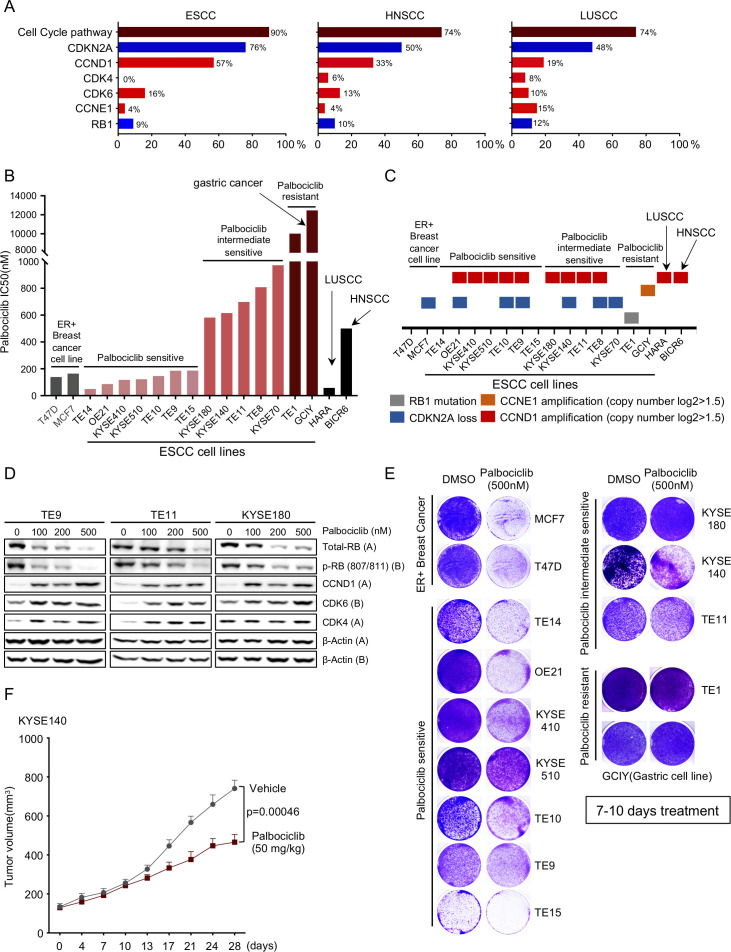
Figure 1.
CDK4/6 inhibitors as a putative target for oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). (A) Frequencies of cell-cycle gene alterations (CDKN2A, CCND1, CDK4, CDK6, CCNE1 and RB1) in OSCC/HNSCC/LUSCC from The Cancer Genome Atlas. Deletion is depicted in blue and amplification is depicted in red. (B) Palbociclib drug sensitivity half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values (nm). Cell lines are coloured as follows: grey: OR positive breast cancer; light red: palbociclib sensitive OSCC; red: palbociclib intermediate sensitive OSCC; dark red: palbociclib resistant OSC line TE1 and gastric line GCIY; black: LUSCC line HARA and HNSCC line BICR6. (C) Annotations of cell-cycle gene alterations in cell lines shown in figure 1B. (D) Immunoblot analysis of genes involved in cell-cycle pathway in OSCC cell lines TE9, TE11 and KYSE180 cells treated with palbociclib (100 nM, 200 nM and 500 nM), or with water control. Protein lysates were collected after drug treatment for 24 hours. Immunoblots from one representative experiment (n=2) are shown. (E) Images showing crystal violet staining of cell lines listed in figure 1B, after 500 nM palbociclib treatment for 7–10 days. Data from one representative experiment are presented (n=3). (F) Growth curve for KYSE140 xenograft tumours (n=6–10) treated with palbociclib (50 mg/kg) by daily gavage. Data are mean±SEM, and p value was calculated by t–tests at 28 days. OR, oestrogen receptor.