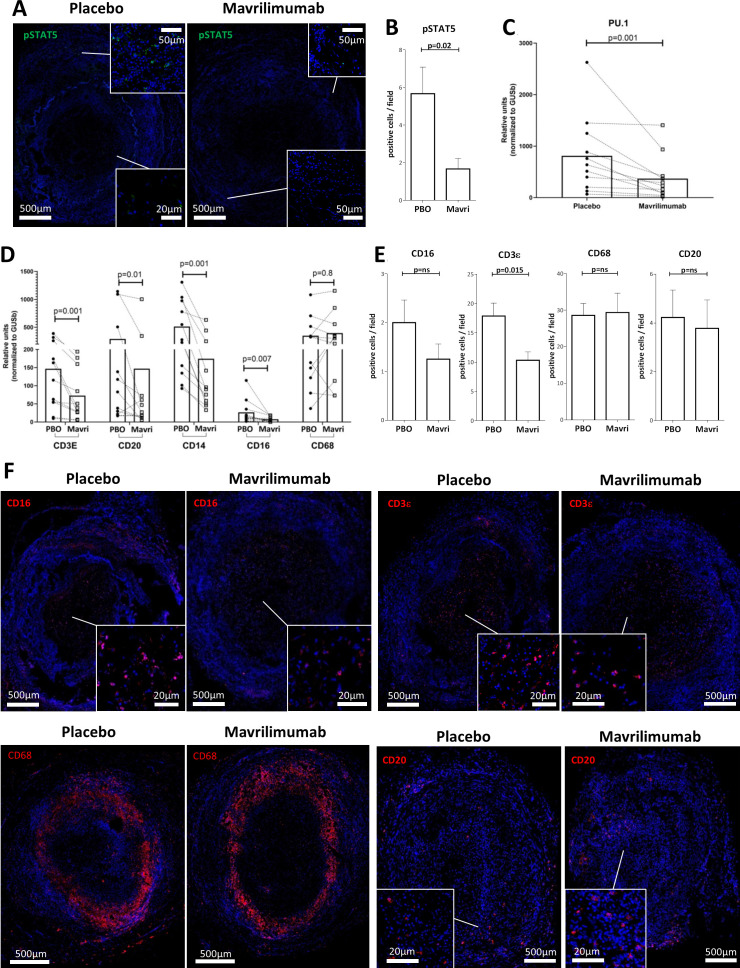
Figure 4.
Effect of mavrilimumab on inflammatory infiltrates in ex vivo cultured arteries from patients with GCA. (A) Immunofluorescence staining with anti-phospho-STAT5 antibody (green) of a GCA artery cultured with placebo or mavrilimumab. (B) Quantification of positive cells per field A; this experiment was performed three times with similar results. (C) mRNA Spl1/PU.1 transcripts in 11 cultured GCA-affected temporal arteries in the presence of placebo or mavrilimumab. (D) Transcript levels for cell markers CD3ε, CD20, CD14, CD16 and CD68 in 11 cultured GCA-involved temporal arteries exposed to placebo or mavrilimumab. (E) Quantification of cells per field that are positive for anti-CD16, anti-CD3Ɛ, anti-CD68, and anti-CD20. (F) Immunofluorescence staining of cultured GCA-involved arteries in the presence of placebo or mavrilimumab with anti-CD16, anti-CD3Ɛ, anti-CD68, and anti-CD20 (red colour) and DAPI (blue). Representative of 3 GCA cultured arteries. Panel E is the quantification of panel F. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GCA, giant cell arteritis.