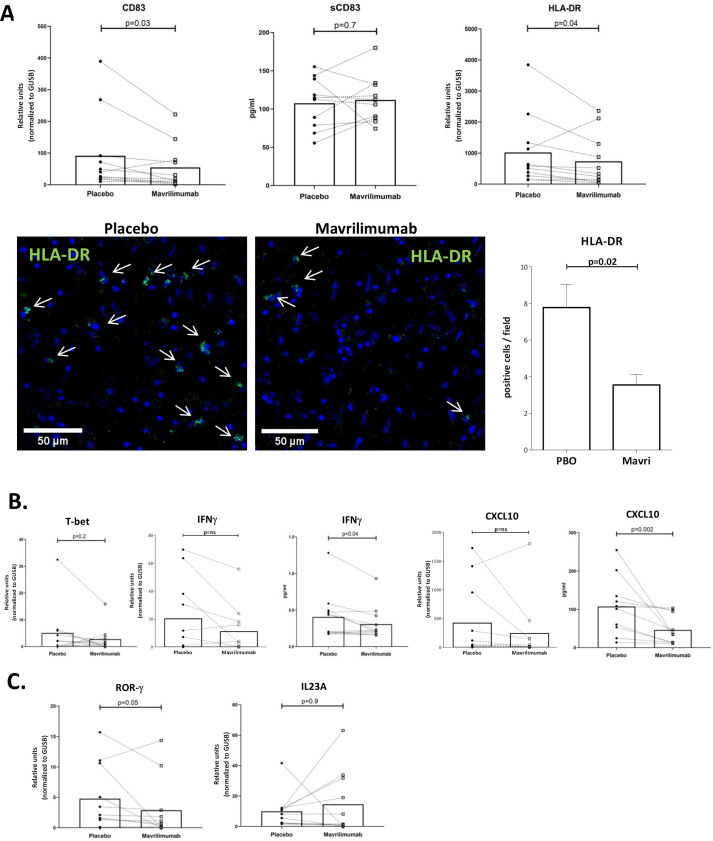
Figure 5.
Mavrilimumab decreases molecules related to T lymphocyte activation and differentiation. (A) mRNA transcripts of CD83 (left) and HLA-DR (right) expressed in relative units and normalised to housekeeping gene GUSB in GCA-positive temporal arteries (n=11) cultured with placebo or mavrilimumab. Soluble CD83 measured (pg/mL) in supernatants of nine GCA cultured arteries exposed to placebo or mavrilimumab (central panel). Image shows HLA-DR expression by immunofluorescence in a GCA artery cultured with placebo or mavrilimumab. Images show detailed zoom amplification by confocal microscope with arrows indicating green HLA-DR-positive cells. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). The graph on the right show the number of HLA-DR-positive cells per field in 9 fields per section. Immunofluorescence was performed in two GCA cultured arteries, with consistent results. (B) mRNA transcripts of TBX21 (T-bet), IFNG (IFNγ) and CXCL10 in GCA arteries cultured with placebo or mavrilimumab (n=11). IFN-γ and CXCL-10 proteins were also measured in artery culture supernatants of the same specimens. Results are expressed in pg/mL. (C) RORC (ROR-γ) and IL-23A mRNA measurement in cultured GCA arteries treated with placebo or mavrilimumab. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GCA, giant cell arteritis; HLA-DR, human leukocyte antigen-DR; IFN, interferon.