Table 1.
A comprehensive list of the reviewed methods/tools for the prediction of prokaryotic promotersa
| Framework | Toolb | Year | Webserver/toolc | Features/Motifs | Scoring function /Algorithm | Evaluation strategy | Promoter typed | Speciese | Sequence length (bp)f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep learning–based | Le et al. [67] | 2019 | Yes* | FastText n-grams | CNN | 5-fold CV | Strong and weak;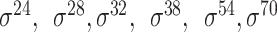 and unknow and unknow |
E. coli | 81 |
| iPromoter-BnCNN [70] | 2020 | Decommissioned | Monomer, trimer and DSP | CNN | 5-fold CV and independent test |
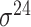 ,
, 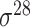 , , 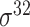 , , 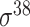 , , 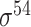 and and 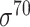
|
E. coli | 81 | |
| Traditional machine learning–based | Leo Gordon et al. [33] | 2003 | Decommissioned | SAK | SVM | 50% train, 50% test | σ 70 | E. coli | 80 |
| Monteiro et al. [36] | 2005 | No | – | Comparative study of NBC, DT, SVM and ANN | Leave-one-out | – | B. subtilis and E. coli | 117, 57 | |
| da Silva et al. [38] | 2006 | No | – | Comparative study of KNN, NBC, DT, SVM and ANN | 10-fold CV | – | B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, B. cereus, B. megaterium, B. thuringiensis, and B. firmus | 111 | |
| Wang et al. [40] | 2006 | No | DSP1, −10 motif scores | Fisher LDA | Independent test | – | E. coli and B. subtilis | 100 | |
| J. J. Gordon et al. [41] | 2006 | Decommissioned | 5-mer tagged with its location, −10 and −35 hexamers | committee-SVM | 10-fold CV | σ 70 | E. coli | 200 | |
| Towsey et al.-I [42] | 2006 | No | 5-mer tagged with its location, −10 and −35 hexamers | SVM | 10-fold CV | σ 70 | E. coli | 200 | |
| pHMM-ANN [39] | 2007 | No | UP element, −10, −35 elements pHMMs | ANN | Independent test | – | E. coli | – | |
| Towsey et al.-II [44] | 2007 | No | Similarity score of candidate TSS, −10, −35 scores, TSS-GSS distance, DSP2 | C4.5 | 10-fold CV | σ 70 | E. coli | 250 | |
| TSS-PREDICT [47] | 2008 | No | −10 and −35 hexamers, 5-mer tagged with its location, TSS- GSS distribution |
Ensemble-SVM | Independent test | σ 70; σ43; σ66 | E. coli, B. subtilis and C. trachomatis | 200 | |
| N4 [48] | 2009 | No | DDS | ANN | Leave-one-out | – | E. coli | 414 | |
| Polat et al. [49] | 2009 | No | 57 sequential DNA nucleotide attributes | Fuzzy-AIRS | 10-fold CV | – | E. coli | 57 | |
| Song et al. [53] | 2012 | Yes* | vw Z-curve | PLS | 10-fold CV |
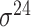 ,
, 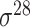 , , 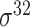 , , 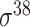 , , 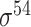 and and 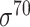 ; ; 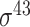 , , 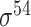 , , 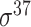 etc. etc. |
E. coli and B. subtilis | 80 | |
| iPro54-PseKNC [55] | 2014 | Yes* | PseKNC | SVM | 10-fold CV and leave-one-out | σ 54 | E. coli | 81 | |
| de Avila e Silva et al. [56] | 2014 | No | DDS | ANN | 2,3,10-fold CV |
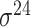 ,
, 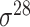 , , 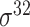 , , 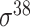 , , 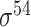 and and 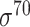
|
E. coli | 80 | |
| bTSSfinder [57] | 2017 | Decommissioned | PE, DPE, k-mer, TFBSD, PCP | ANN | Independent test |
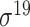 ,
, 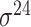 , , 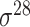 , , 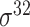 , , 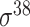 , , 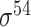 and and 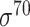
|
E. coli, S. elongatus, Nostoc, and Synechocystis | 251, 1101 | |
| iPromoter-2L [58] | 2018 | Yes | PseKNC | RF | 5-fold CV |
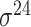 ,
, 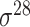 , , 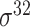 , , 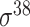 , , 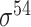 and and 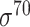
|
E. coli | 81 | |
| 70ProPred [59] | 2018 | Yes | PSTNPSS/PSTNPDS, PseEIIP | SVM | 5-fold CV and leave-one-out | σ 70 | E. coli | 81 | |
| IBPP-SVM [60] | 2018 | Yes* | ‘image’ | SVM | Independent test | σ 70 | E. coli | 81 | |
| BacSVM+ [61] | 2018 | Decommissioned | – | SVM | – |
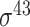 ,
, 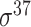 , , 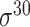 , , 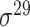 , , 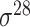 and and 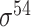
|
B. subtilis | 80 | |
| iPro70-PseZNC [62] | 2019 | Yes | PseZNC | SVM | 5-fold CV | σ 70 | E. coli | 81 | |
| iPromoter-FSEn [63] | 2019 | Yes | k-mer, g-gapped k-mer, NSM, ASPC, PSO, DN | SVM, LDA, LR | 10-fold CV and leave-one-out | σ 70 | E. coli | 81 | |
| iPro70-FMWin [64] | 2019 | Yes | k-mer, g-gapped k-mer, NSM, ASPC, PSO | LR | 10-fold CV | σ 70 | E. coli | 81 | |
| iPSW(2L)-PseKNC [65] | 2019 | Yes | General PseKNC | SVM | 5-fold CV | Strong and weak;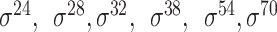 and unknow and unknow |
E. coli | 81 | |
| MULTiPly [66] | 2019 | Yes | BPB, KNN, KNC, DAC | SVM | 5-fold CV, leave-one-out and independent test |
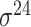 ,
, 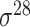 , , 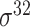 , , 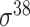 , , 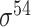 and and 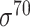
|
E. coli | 81 | |
| iPromoter-2L2.0 [68] | 2019 | Yes | k-mer, PseKNC | SVM, EL | 5-fold CV |
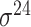 ,
, 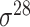 , , 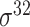 , , 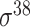 , , 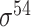 and and 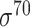
|
E. coli | 81 | |
| SELECTOR [69] | 2020 | Yes | CKSNAP, PCPseDNC, PSTNPss and DNA strand | RF, AdaBoost, GBDT, LightGBM, XGBoost | 5-fold CV and independent test |
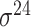 ,
, 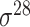 , , 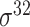 , , 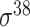 , , 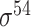 and and 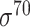
|
E. coli | 81 | |
| Scoring function–based | Huerta et al. [34] | 2003 | No | −10 and −35 box, spacer between −10 and −35 box | PWM | Independent test | σ 70 | E. coli | 250 |
| TLS-NNPP [35] | 2005 | No | TSS-TLS distance, the results from NNPP2.2 | Probability 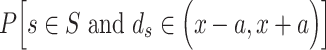
|
Independent test | – | E. coli | 500 | |
| Kanhere et al. [37] | 2005 | No | DDS | DE | Independent test | – | E. coli, B. subtilis and C. glutamicum | 1000 | |
| Li et al. [43] | 2006 | No | Hexamer sequence conservation | PCSF | 10-fold CV | σ 70 | E. coli | 81 | |
| Beagle [72] | 2006 | Decommissioned | UP element, −10, −35 and extended −10 elements, and TSS-GSS gap | PWM | 10-fold CV | σ 70 | E. coli and B. subtilis | 250 | |
| Footy [45] | 2007 | Decommissioned | −10 and −35 hexamers | PWM | Independent test | σ 66 | C. trachomatis, C. pneumoniae, C. caviae and C. muridarum | – | |
| Rangannan et al. [46] | 2007 | No | DDS | DE | Independent test | – | E. coli and B. subtilis | 101, 1001 | |
| PromPredict [50] | 2009 | Yes* | DDS | DE | Independent test | – | E. coli, B. subtilis and M. tuberculosis | 1001 | |
| PromPredict [51] | 2010 | Yes* | DDS, GC content | DE | Independent test | – | 913 bacteria in PromBase [183] | 1001 | |
| BacPP [52] | 2011 | Yes | Rules extracted from neural networks | Weighting promoter prototypes | 2, 3, 10-fold CV |
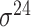 ,
, 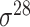 , , 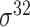 , , 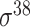 , , 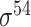 and and 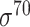
|
E. coli | 80 | |
| Todt et al. [54] | 2012 | No | −10, −35 and extended −10 elements | PWM | Independent test | σ 70 | L. plantarum | 100 | |
| G4PromFinder [71] | 2018 | Yes* | AT-rich element and G-quadruplex motif | – | Independent test | – | S. coelicolor and P. aeruginosa | 251 |
aAbbreviations: CNN—convolutional neural network; CV—cross-validation; DSP—DNA structural property; SAK—sequence alignment kernel; SVM—support vector machine; TSS-TLS distance—the distance between the transcription start site (TSS) and the translation start site (TLS); TDNN—time-delay neural network; NBC—naïve Bayes classifier; DT—decision tree; ANN—artificial neural network; KNN—k-nearest neighbor; DSP1—SIDD, curvature, deformability, thermodynamic stability; SIDD—stress-induced DNA duplex destabilization; LDA—linear discriminant analysis; committee-SVM—DGS, PWM and ensemble SVM; DGS—the distribution of TSS distance to gene start; PWM—position weight matrix; pHMMs—profile hidden Markov models; DSP2—DNA curvature, SIDD, stacking energy; DDS—DNA duplex stability; Fuzzy-AIRS—Artificial Immune Recognition System with Fuzzy resource allocation mechanism; vw Z-curve—variable-window Z-curve; PLS—partial least squares; PseKNC—pseudo–K-tuple nucleotide composition; PE—promoter elements including −10, −35, −15 and AT-rich UP elements, together with the new TSS motifs by the authors; DPE—distances (d) between promoter elements (contains d(−10/−35), d(−10/TSS) and d(−15/−10)); TFBSD—TFBSs density; PCP—physico-chemical properties (i.e. free energy, base stacking, entropy and melting temperature); RF—random forest; PSTNPSS/PSTNPDS—position-specific trinucleotide propensity based on single-stranded or double-stranded characteristic, PseEIIP—electron–ion interaction pseudo-potentials of trinucleotide; PseZNC—pseudo–multi-window Z-curve nucleotide composition; NSM—nucleotide statistical measure; ASPC—approximate signal pattern count; PSO—position specific occurrences; DN—distribution of nucleotides; LR—logistic regression; BPB—bi-profile Bayesian signatures; KNC—k-tuple nucleotide composition; DAC—dinucleotide-based auto-covariance; EL—ensemble learning; CKSNAP—composition of k-spaced nucleic acid pairs; PCPseDNC—parallel correlation pseudo-dinucleotide composition; GBDT—gradient boosting decision tree; DE—relative stability (the difference in free energy); PCSF—position-correlation scoring function.
bThe URL addresses for the listed tools: iPro54-PseKNC—http://lin-group.cn/server/iPro54-PseKNC; iPromoter-2L—http://bioinformatics.hitsz.edu.cn/iPromoter-2L/; 70ProPred—http://server.malab.cn/70ProPred/; iPro70-PseZNC—http://lin-group.cn/server/iPro70-PseZNC; iPro70-FMWin—http://ipro70.pythonanywhere.com/server; iPromoter-FSEn—http://ipromoterfsen.pythonanywhere.com/server; iPSW(2L)-PseKNC—http://www.jci-bioinfo.cn/iPSW(2L)-PseKNC; MULTiPly—http://flagshipnt.erc.monash.edu/MULTiPly/; iPromoter-2L2.0—http://bliulab.net/iPromoter-2L2.0/; SELECTOR—http://SELECTOR.erc.monash.edu/; PromPredict— http://nucleix.mbu.iisc.ernet.in/prompredict/prompredict.html; BacPP—http://bacpp.bioinfoucs.com/home.
cYes—The approach is accompanied with a webserver/tool and it is still working; Decommissioned—The webserver/tool is no longer available; No—The approach has no webserver or tool; Yes*—The server/tool was not involved in our performance comparison due to the unavailable pretrained model, unavailable latest test data or the unmatched sequence length.
dWe listed the detailed prokaryotic promoter types based on the description in the papers. ‘–’ demonstrates such information is not present in the paper.
eThe species information of the sequences used in corresponding studies was directly extracted from the studies. For some species, the Latin names have been provided according to the predictors; for other species, based on the information provided in the papers, we just provided the general names of the species when their Latin names are not available.
f‘–’ demonstrates that no clearly length information is provided in the paper.
