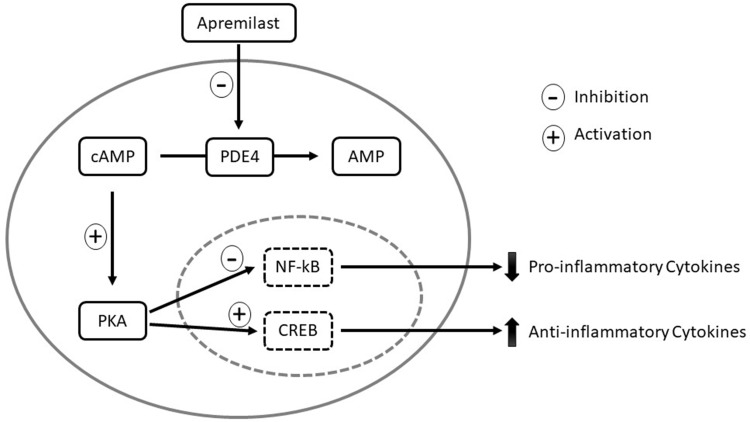
Figure 1.
Mechanism of action of apremilast. In monocytes and dendritic cells, PDE4 degrades cAMP to AMP. When apremilast inhibits PDE4, intracellular cAMP levels increase and activate PKA. PKA activation results in phosphorylation of the transcription factors CREB and NF-κB. Phosphorylation leads to activation of CREB, which increases anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10. Phosphorylation of NF-κB results in inhibition of transcriptional activity, thereby decreasing expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-23, TNF-α, and IFN-γ. The decreased production of inflammatory mediators reduces inflammation and proliferation of keratinocytes in psoriatic skin.
Abbreviations: cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CREB, cAMP responsive element-binding protein; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; PDE4, phosphodiesterases; PKA, protein kinase A; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha.