Extended Data Fig. 9 |. Genomic instability (GI), homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) and Chromothripsis (CHTP) across the cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) with race classified by inferred ancestry.
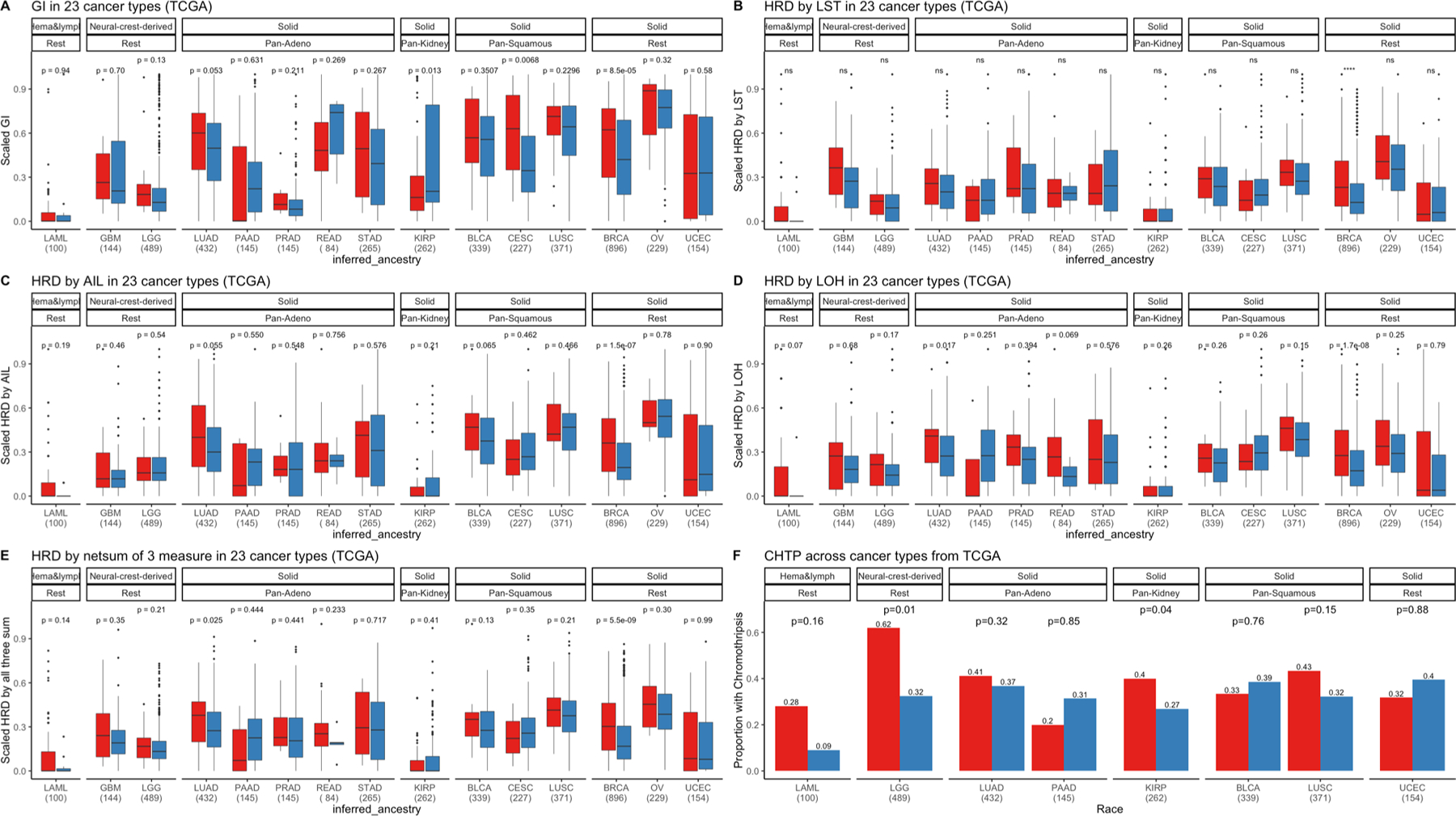
a, HRD based on number large-scale state transitions (LST) (b), telomere allelic Imbalance (AIL) (c), number of LOH events (d) and scaled net sum of previous three defined as “genomic scar” (e), and CHTP (f) Is quantified and presented In European Americans (EAs) and African Americans (AAs) in various cancer types in TCGA where sample size for each cancer type is provided on the x-axis. First, cancer types are categorized by cell type or tissue of origin, if possible, where defined groups are pan-squamous (squamous cell derived tumors), panadeno (glandular structures in epithelial tissue derived tumors), pan-kidney (tumors originating in the kidney), and rest (referring to cancer types that cannot be categorized and includes LAML, GBM, LGG, BRCA, OV, and UCEC). Refer here for reference to cancer types for reference: https://gdc.cancer.gov/resources-tcga-users/tcga-code-tables/tcga-study-abbreviations). Second, additional categorization was performed based on tissue type (where solid is derived from solid tumors and neural-crest and Hema & Lymph—hematologic and lymphatic tumors). Across, panels a-e, two-sided Wilcoxon Rank-sum test has been performed for each cancer type and significance before multiple testing correction is provided. In the corresponding panels, the box plot, the center line denotes the median, the box indicates the interquartile range and the black line represents the rest of the distribution, except for points that are determined to be “outliers”, 1.5 times the interquartile range. In panel f, one-sided Fisher test has been performed to test whether chromothripsis frequency is higher in AA or not.
