Figure 5.
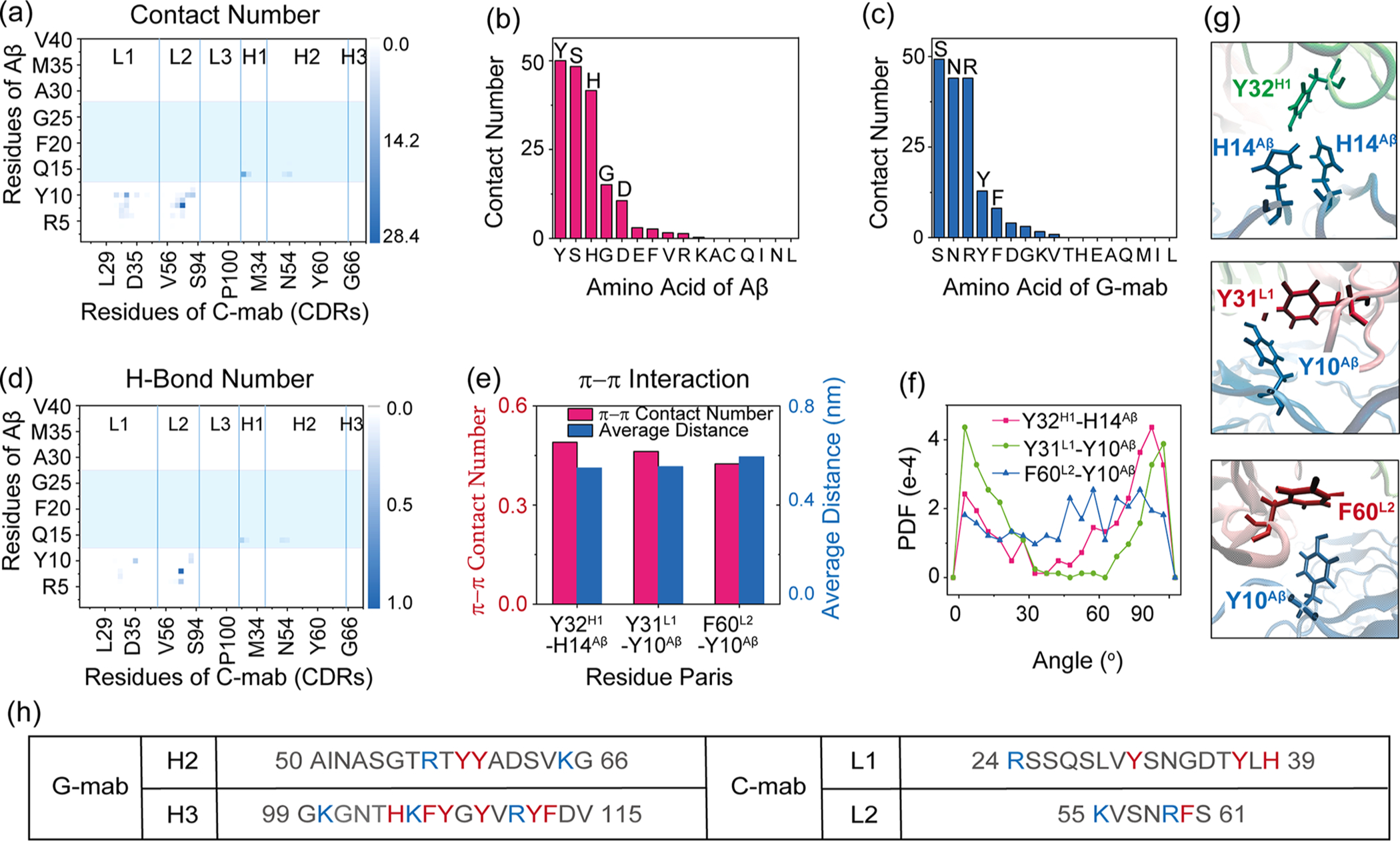
C-mab-Aβ4016mer interactions in system C-MD1. (a) Contact probabilities between each residue of C-mab and Aβ40 fibril. (b, c) Total contact number for each residue type of Aβ with antibody (b) and each residue type of antibody with Aβ (c). (d) Map of H-bond number between C-mab and Aβ4016mer. (e–g) π–π interactions between C-mab and Aβ4016mer: (e) π–π stacking number and average distance between two aromatic rings; (f) PDF of dihedral angle between two aromatic planes; (g) snapshots showing aromatic interactions. (h) Comparison of the sequences of the two CDRs in C-mab and G-mab that contribute most to antibody–Aβ4016mer contact. Residues with positive charge are colored in blue, while aromatic residues are colored in red.
