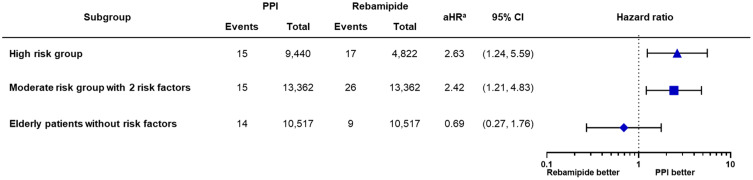
Figure 3.
The effect of PPI and rebamipide on the tNSAID-induced serious GI complication risk according to the risk group.
Notes: aHistory of serious GI bleeding or perforation, non-serious peptic ulcer disease, cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, inflammatory bowel disease, hemorrhagic stroke, cancer, alcoholism, gastroesophageal reflux disease, thrombocytopenia, heart failure, hypertension, CCI score, number of risk factors, concomitant use of anticoagulants, antiplatelets, steroids, and SSRIs, age and sex were included as covariates for adjustment.
Abbreviations: aHR, adjusted hazard ratio; CCI, Charlson Comorbidity Index; CI, confidence interval; GI, gastrointestinal; PPI, proton-pump inhibitor; SSRI, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; tNSAID, traditional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.