Figure 2. Molecular signaling pathways involved in CCM lesion formation.
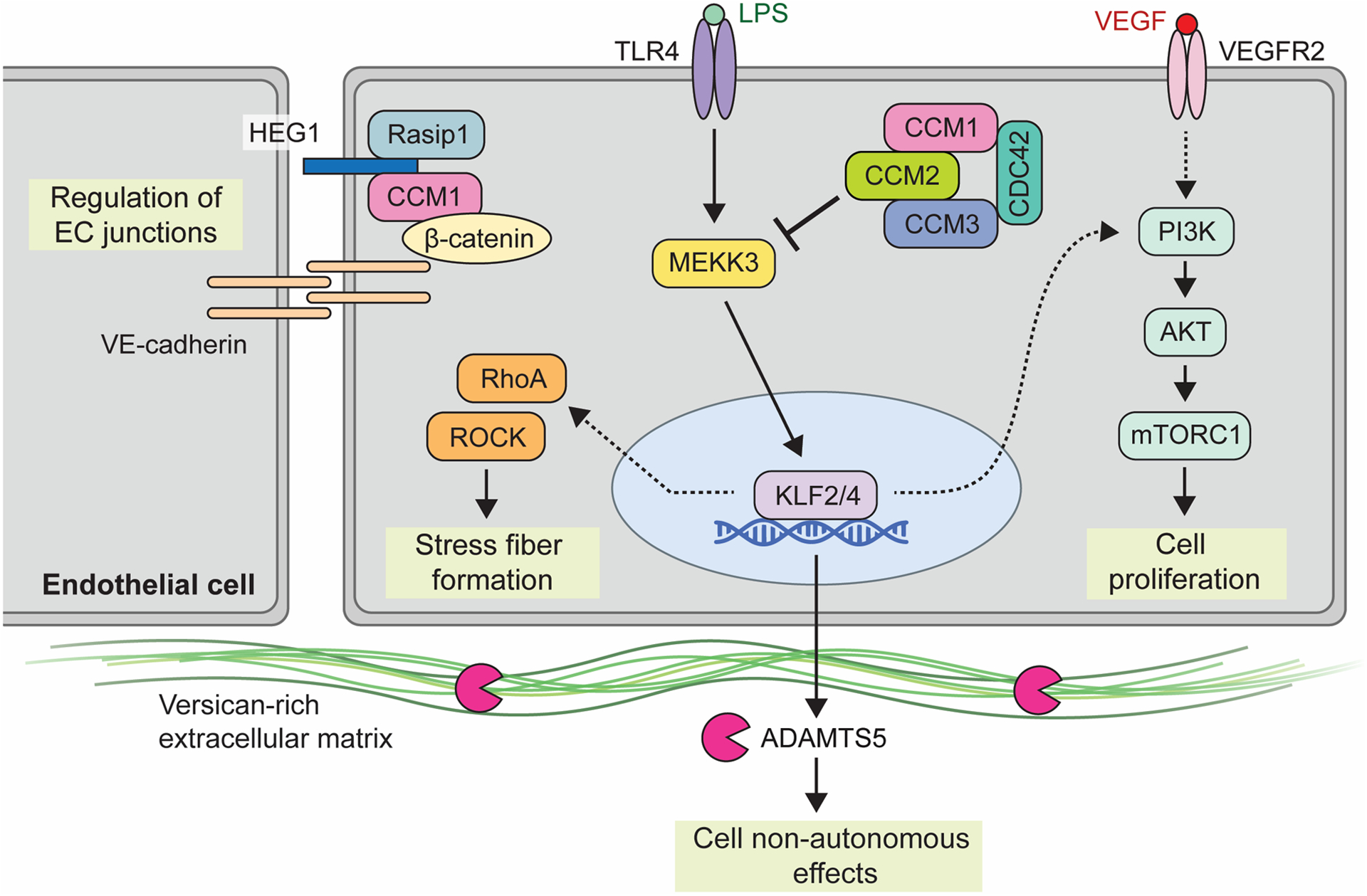
Shown is a partial summary of the various upstream inputs and downstream effectors implicated in CCM signaling. The heterotrimeric CCM complex, consisting of CCM1 (KRIT1), CCM2, and CCM3 (PDCD10), is an inhibitor of MAP3K3 Kinase, MEKK3. Inflammatory signals via TLR4 serve as the upstream input into MEKK3 signaling, as may shear forces associated with blood flow (not shown). Loss of CCM and subsequent activation of MEKK3 leads to upregulation of transcription factors KLF2 and KLF4. Downstream KLF2/4 transcriptional targets include both cell autonomous pathways through PI3K signaling and RHO/ROCK signaling, as well as cell non-autonomous effects via metalloprotease ADAMTS5 and extracellular matrix cleavage. VEGF is shown as a possible distinct input for PI3K-mTOR signaling while HEG1 has been associated with regulation of endothelial cell junctions. Of note, numerous other pathways have been found to be affected by loss of CCM function. This diagram focuses on those that are presently best understood and those that have been investigated using mouse and human genetic studies and/or are presently targeted therapeutically.
