Figure 4. Mechanism of increase in TM and EPCR in CCM.
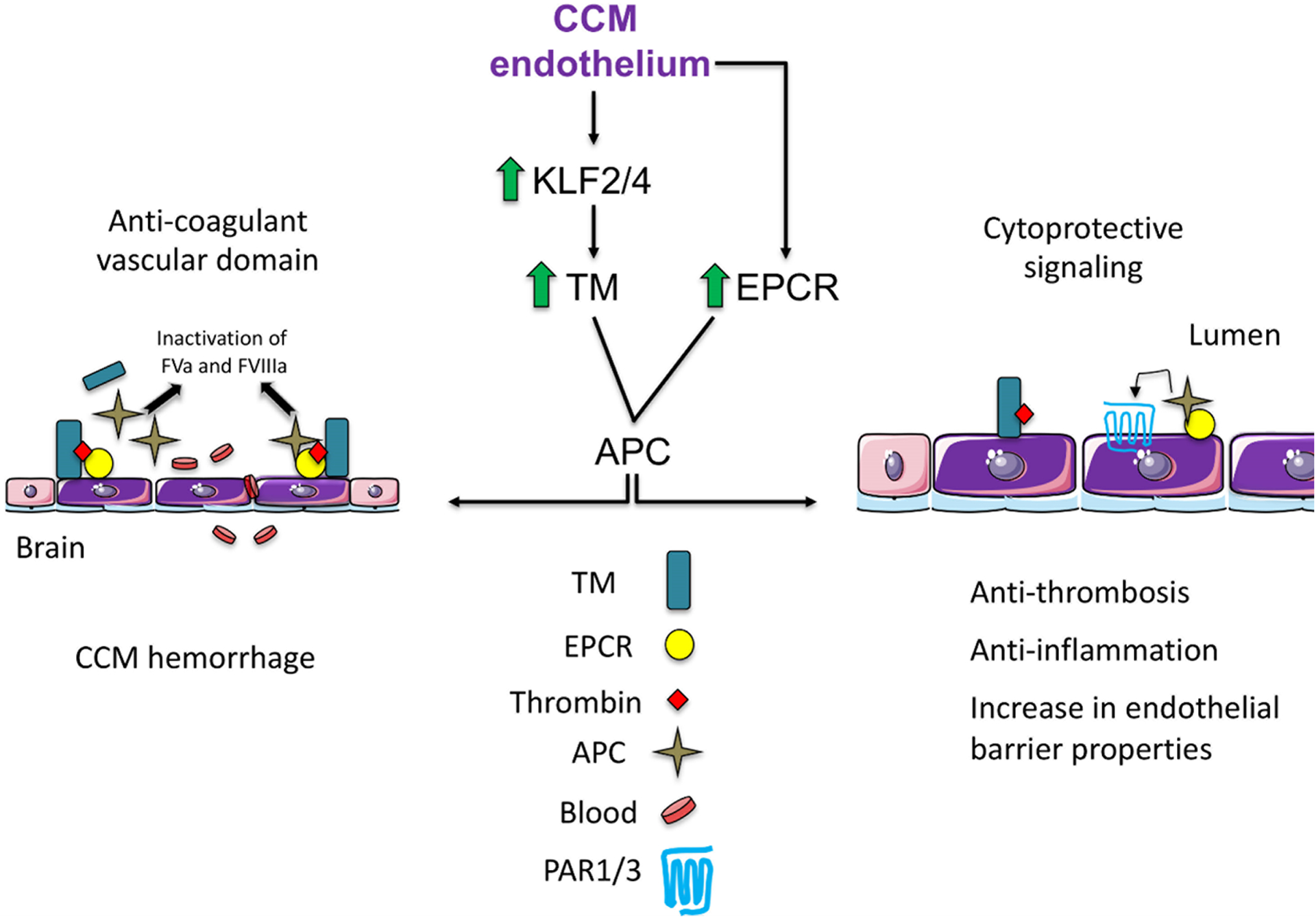
CCM endothelium is associated with locally elevated expression of anticoagulant endothelial receptors TM and EPCR. TM upregulation is due to upregulation of KLF2 and KLF4 transcription factors. Increased levels of vascular TM and EPCR result in enhanced APC and the anticoagulation cascade by inactivation of FVa and FVIIIa, thus contributing to an increase in lesion bleeding (Anti-coagulant vascular domain). Proposed cytoprotective signaling in CCMs, retention of APC to endothelial receptor EPCR allows activation of PAR1/3 and subsequent cytoprotective signaling in CCM endothelium. TM-thrombin complex reduces fibrin generation, and TM exerts anti-inflammatory properties. TM=thrombomodulin, EPCR= endothelial protein C, APC=activated protein C. Adapted from Lopez-Ramirez et al.121 and Mosnier et al.152
