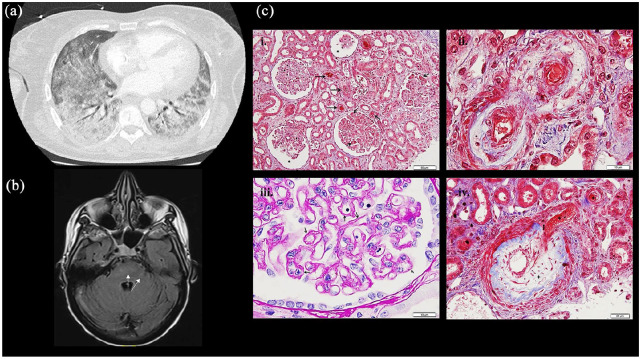
Figure 1.
Capture of different clinical manifestations: (a) Chest CT scan: Bilateral interstitial diffuse syndrome on the CT (lung window), (b) brain MRI (Flair axial) with evidence of hypersignal in the right cerebellar hemisphere axial plan of Flair sequence, (c) renal biopsy ((i)–(iv)): (i) Glomeruli show ischemic features with thickening of the glomerular capillary basement membranes and/or dilated urinary space (*). Many thrombosis or red blood cells are seen in arterioles and capillary lumen of glomeruli (→). (Masson’s trichrome, ×200). (ii). Mucoid intimal thickening with considerable reduction of the interlobular arterial lumen (+) with red blood cells are seen in vascular luminary of small afferent arteries (*). (Masson’s trichrome, ×400). (iii). Pale mucoid intimal hyperplasia of a small interlobular artery, with swelling of medial myocytes (*). (Masson’s trichrome, ×1000). (iv). Thickening and wrinkling of the glomerular capillary wall with double-contour appearance (→). (Periodic-acid Schiff, ×1000).