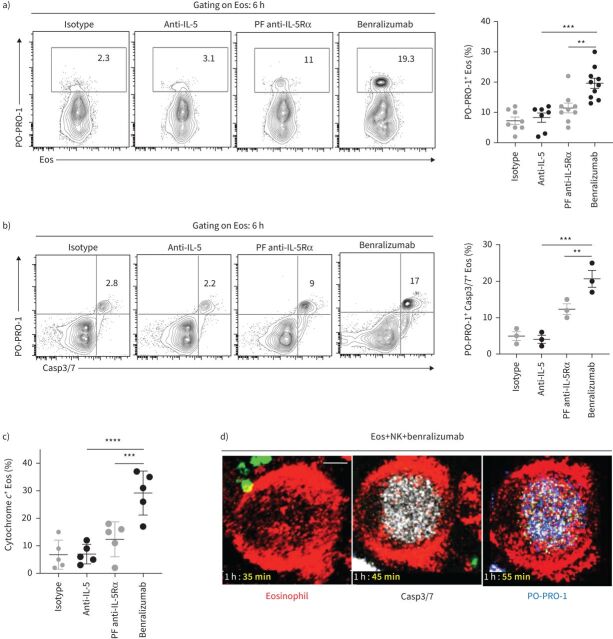
FIGURE 1.
Benralizumab induces caspase-dependent eosinophil (Eos) apoptosis by natural killer (NK) cells. Primary human NK cells and eosinophils isolated from healthy donors were labelled individually. NK cells were loaded with LysoTracker Green to selectively label NK lytic granules. Eosinophils were pre-treated with 10 nM of the indicated antibodies, then mixed with NK cells for 6 h and analysed. a–c) Eosinophil cell death, evaluated by PO-PRO-1 blue dye for detection of a) apoptotic and dead cells (n=7), b) caspase activation assessed by CellEvent Caspase-3/7 (Casp3/7) reagent (n=3), and c) cytochrome c (n=3), represented as percentage of total CD66b+ Siglec-8+ eosinophils. Data are mean±sem. d) Representative frames selected from live imaging data, with 10 min intervals, displaying caspase activation in eosinophils with CellEvent Caspase-3/7 reagent, indicated in white. Confocal microscopy was used for live imaging for 90 min. Images were acquired every 5 min. Scale bar: 2 µm (n=4). Two-way ANOVA was employed with Tukey's multiple comparisons. **: p<0.01; ***: p<0.001; ****: p<0.0001, benralizumab versus controls (anti-interleukin (IL)-5 or parent fucosylated anti-IL-5 receptor α (PF anti-IL-5Rα)). Statistical values are presented in supplementary table S2.