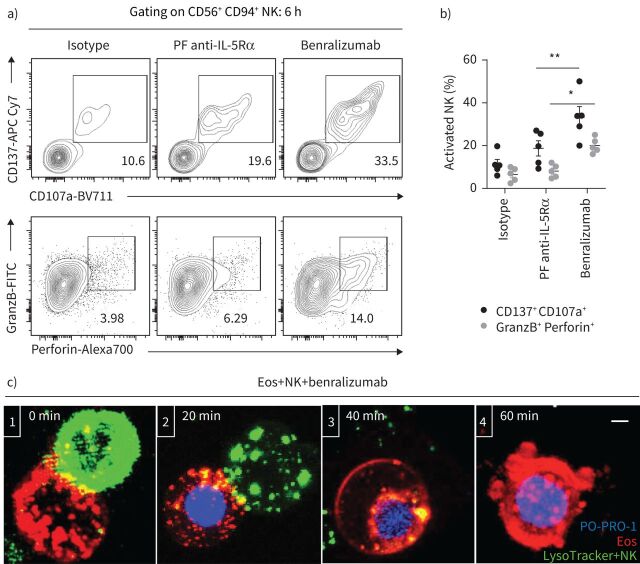
FIGURE 2.
Natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxicity mediates benralizumab-induced eosinophil (Eos) apoptosis. Primary eosinophils and NK cells were prepared as described in figure 1. a, b) Changes in NK activation (CD137 and CD107a) and NK cytolytic (granzyme B (GranzB) and perforin) markers: a) assessed by flow cytometry and b) represented as percentage of total CD56+ CD94+ NK cells (n=4). Data are mean±sem. c) Stepwise stages of NK-mediated eosinophil death induced by benralizumab. Cells were live imaged by confocal microscopy for 90 min. The images are representative frames acquired approximately every 2 min. 1) NK immunological synapse is established between a NK cell and an eosinophil. 2) NK lytic granules are docked at the cellular interface of the eosinophil initiating cell death as PO-PRO-1 enters the cell. 3) NK detaches from the eosinophil after delivery of NK lytic granules. 4) The eosinophil undergoes apoptosis as indicated by chromatin condensation, membrane blebbing and nuclear collapse. Scale bar: 2 µm. Two-way ANOVA was employed with Tukey's multiple comparisons. *: p<0.05; **: p<0.01, benralizumab versus parent fucosylated anti-interleukin-5 receptor α (PF anti-IL-5Rα). Statistical values are presented in supplementary table S2.