FIGURE 3.
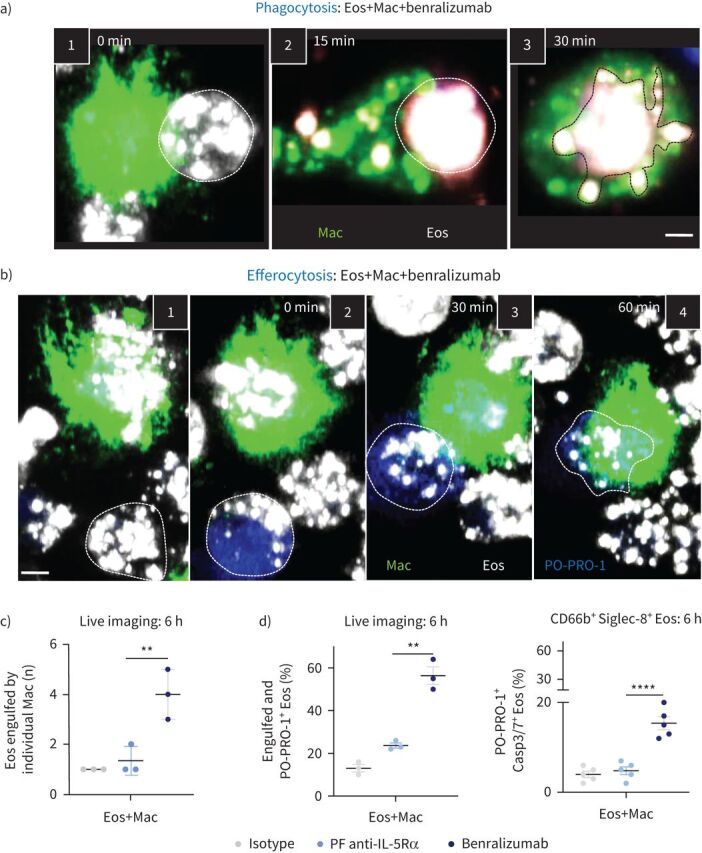
Documenting the steps of benralizumab-mediated eosinophil (Eos) depletion by macrophage (Mac) phagocytosis or efferocytosis. Human primary natural killer (NK) cells and eosinophils isolated from healthy donors were labelled individually. Macrophages were stained with green lipid membrane dye. Eosinophils were pre-treated with 10 nM of benralizumab then labelled with red lipid membrane dye. Red-labelled eosinophils were co-incubated with green-labelled NK cells in the presence of PO-PRO-1 for detection of cell death. Conjugates were live cell imaged by confocal microscopy for 90 min. a) Stepwise stages of macrophage-mediated eosinophil phagocytosis targeted by benralizumab. 1) Macrophage–eosinophil immune synapse is established. 2) Formation of the phagocytic cup. 3) Eosinophil internalisation by macrophages. b) Stepwise stages of macrophage-mediated eosinophil efferocytosis. 1, 2) Eosinophil undergoing apoptosis prior to 3) uptake and 4) engulfment by macrophages. c) Quantification of eosinophils engulfed by individual macrophages post-treatment with the indicated antibodies via live imaging (n=5). d) Left: quantification of eosinophil death (macrophage-engulfed and PO-PRO-1+ eosinophils) by live imaging, as percentage of total far-red-labelled eosinophils (n=3), in the presence of macrophages; right: changes in caspase activation assessed by flow cytometry using CellEvent Caspase-3/7 (Casp3/7) reagent and represented as percentage of total CD66b+ Siglec-8+ eosinophils (n=3). a, b) Images are frames acquired approximately every 5 min, then representative frames were selected with 15 or 30 min intervals for illlustration. Scale bar: 2 µm. c, d) Data are mean±sem. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey's and Šídák's multiple comparisons. **: p<0.01; ****: p<0.0001, benralizumab versus parent fucosylated anti-interleukin-5 receptor α (PF anti-IL-5Rα). Statistical values are presented in supplementary table S2.
