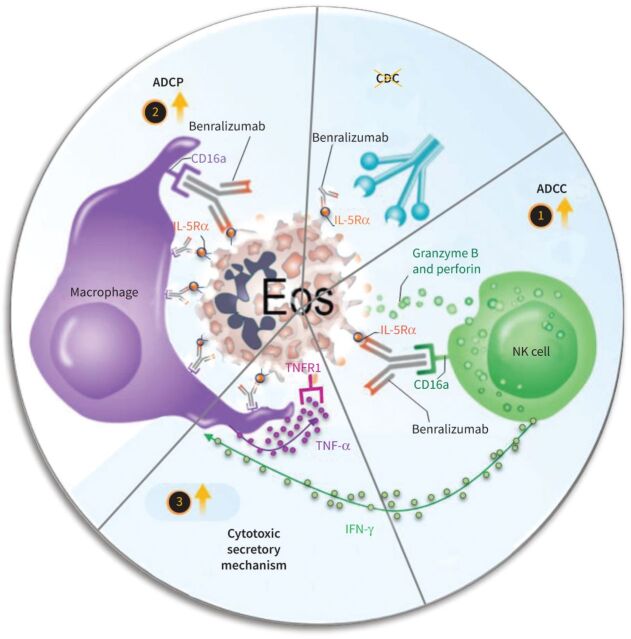
FIGURE 8.
Proposed mechanisms for benralizumab-induced eosinophil (Eos) depletion through antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) and tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-dependent macrophage cytotoxicity. 1) In the ADCC process, benralizumab induced eosinophil apoptosis by activated natural killer (NK) cells. 2) Also, benralizumab promoted ADCP by macrophages to deplete eosinophils either by phagocytosis or efferocytosis. 3) Activated NK cells release stimulatory factors such as interferon-γ (IFN-γ) to induce macrophage cytotoxicity through TNF-α that can trigger TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1)-dependent eosinophil apoptosis; these apoptotic cells are removed by macrophage efferocytosis. Lastly, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) seems not to be involved in benralizumab-mediated eosinophil depletion. IL-5Rα: interleukin-5 receptor α.