Figure 7.
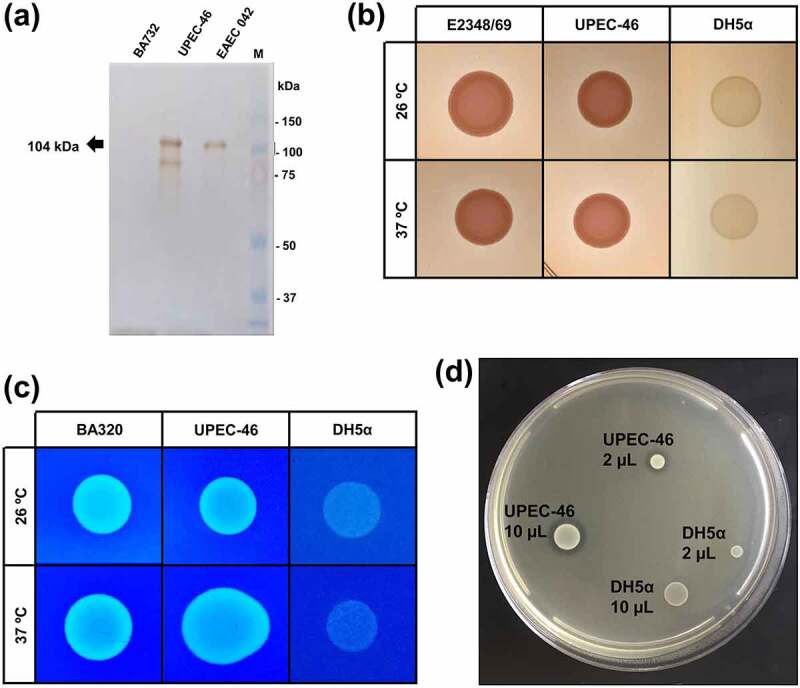
Phenotypic characteristics of UPEC-46. (a) Pet detection in the UPEC-46 using culture supernatants. The bacterial supernatants were cultivated in LB and precipitated with Trichloroacetic acid (TCA). Immunoblotting was performed with anti-Pet IgG and developed with Diaminobenzidine. Positive control: EAEC 042. Negative control: EAEC BA732. M: Precision plus protein™ dual color standards (Bio-Rad, USA) used as molecular weight. (b) Analysis of curli expression using the Congo red agar at 26°C and 37°C. EPEC E2348/69 and E. coli DH5α represent positive and negative controls, respectively. (c) Cellulose expression using the cellulose agar at 26°C and 37°C. E. coli BA320 and DH5α were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. (d) Bacteriocin production of UPEC-46. A drop of 2 and 10 μL of the overnight culture (UPEC-46 and negative control) was placed on a plate containing a freshly prepared lawn of E. coli C600 (indicator strain for bacteriocin production). After overnight incubation at 37°C, the plate was examined for clear zones. E. coli DH5α was used as a negative control
