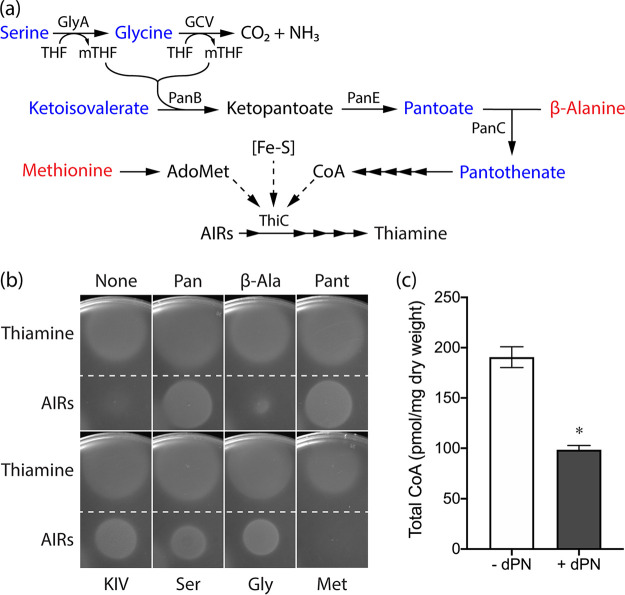
FIG 6.
Precursors for CoA synthesis eliminate dPN sensitivity of a ptsJ mutant. (a) The integrated serine-glycine metabolic node, CoA, and thiamine synthesis in S. enterica. Blue indicates metabolites that mitigate the inhibition of dPN on ThiC-dependent thiamine synthesis, while those in red have little to no effect. Solid arrows indicate biochemical reactions in the pathways. Dashed arrows depict metabolic processes that affect ThiC activity. (b) The purGE stm4068 ptsJ strain (DM17274) was mixed with soft agar and overlaid onto minimal NCE glucose containing adenine (0.4 mM) and dPN (0.1 μM) without or with one of the following supplementations: pantothenate (0.1 mM), pantoate (0.1 mM), β-alanine (0.1 mM), KIV (0.1 mM), serine (2.5 mM), glycine (0.67 mM), or methionine (0.3 mM). The AIRs requirement was assessed by spotting 1 μL of AIRs (∼300 mM) and thiamine (0.1 mM) as a control. (c) Total intracellular CoA level of a ptsJ mutant (DM17239) grown in minimal NCE glucose in the absence or presence of dPN (0.5 μM). *, P < 0.0001, as determined by two-tailed unpaired Student's t test. Representative data from two experiments, each with three biological replicates, are shown. Error bars depict standard deviations from the means. THF, tetrahydrofolate; Pan, pantothenate; β-Ala, β-alanine; Pant, pantoate; Ser, l-serine; Gly, l-glycine; Met, l-methionine.