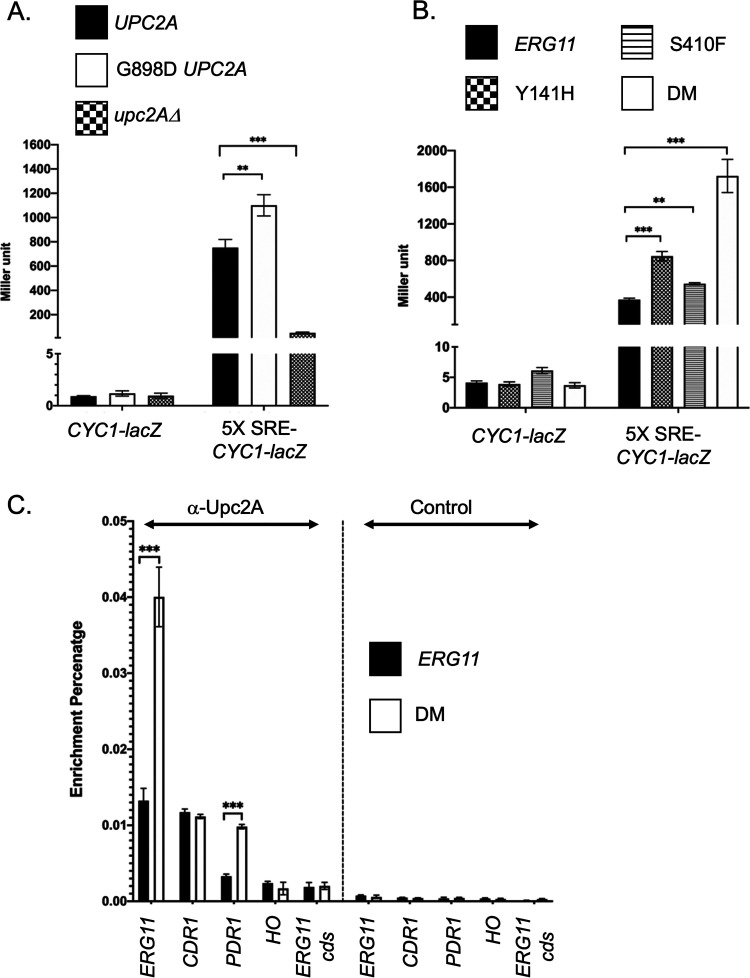
FIG 4.
Regulation of Upc2A in response to ERG11 alleles. A. Two different reporter constructs carried on low-copy-number C. glabrata vectors that contained either the S. cerevisiae CYC1 promoter region with a translational fusion to E. coli lacZ (CYC1-lacZ) or the same reporter construct with five copies of the C. glabrata ERG1 sterol response element (SRE) cloned upstream of the CYC1 promoter (5X SRE-CYC1-lacZ) were introduced into the three different C. glabrata strains indicated at the top. These strains varied at their UPC2A allele corresponding to a wild-type strain (UPC2A), gain-of-function form of UPC2A (G898D UPC2A) or a null mutation (upc2AΔ). Transformants were grown to mid-log phase and then assayed for the level of β-galactosidase produced in each strain. B. The two different reporter plasmids from A were introduced into the 4 isogenic ERG11 mutant strains indicated. Transformants were grown to mid-log phase and assayed for β-galactosidase levels. C. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) of Upc2A DNA-binding to genomic target sites. Total sheared and cross-linked chromatin was prepared from either wild-type or DM ERG11 cells. ChIP reactions were carried out with either anti-Upc2A or a nonspecific control antisera. Immunopurified DNA was quantitated with qPCR using primer pairs that detected the promoters of ERG11 (ERG11), CDR1 (CDR1), PDR1 (PDR1) or HO (HO) along with a primer pair that detected a segment of the ERG11 coding sequence (ERG11 cds). Data are plotted as the percentage of DNA recovered in the immunopurified sample/total input DNA.