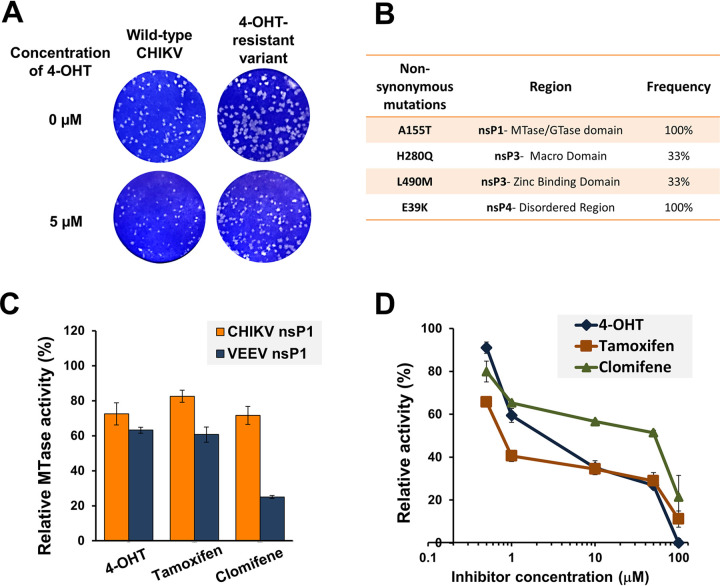
FIG 4.
The nsP1 capping enzyme is implicated in alphavirus inhibition by SERMs. Altered plaque phenotype of the partially resistant variant of CHIKV against 4-OHT. (A) Standard plaque assay performed on the indicated virus. Vero cells were overlaid with 1% carboxymethyl cellulose-containing medium either without or with 5 μM 4-OHT. Plaques were visualized 48 hpi using crystal violet. A plaque-purified variant harboring all four mutations was used for phenotypic characterization. The resistant variant replicates more efficiently than wild-type CHIKV both in terms of number and size of plaques in the presence of 4-OHT. (B) Nonsynonymous mutations in the nsP-coding region of a partially resistant CHIKV variant. Mutations were identified with the sequencing of three independent plaque-purified viruses. (C) nsP1 MTase activity inhibition by tested compounds. SERM compounds were tested at a concentration of 50 μM in the CHIKV nsP1 (10 μM) and VEEV nsP1 (20 μM) MTase reaction mixture. The reaction was carried out as described previously by Mudgal et al. (12). The MTase activity is shown relative to the enzyme activity in the reaction mixture in the presence of vehicle control. (D) Dose-dependent inhibition of guanylation of nsP1 in the presence of SERMs. Relative guanylation by CHIKV nsP1 was determined using an ELISA that measures the amount of m7GMP-nsP1 adduct formed in the reaction. Reaction conditions were similar to those described earlier by Kaur et al. (29). Data points represent mean value, and error bars are the standard deviation from two independent experiments.