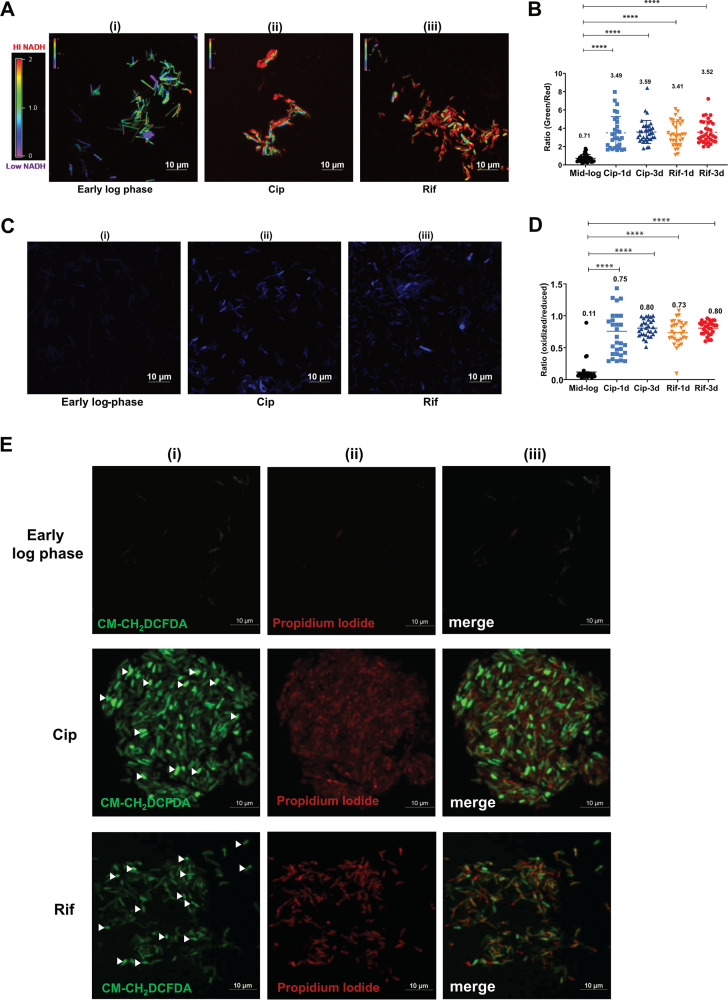
FIG 2.
Analysis of redox imbalance and ROS levels in antibiotic persisters. (A) Ratiometric analysis of NADH/NAD+ levels in APs. After 72 h of treatment, the Cip and Rif APs of M. smegmatis harboring Peredox-mCherry were imaged along with an untreated early-mid-log-phase culture. The images were assigned a pseudocolor for the representation of the NADH:NAD+ levels in individual cells. (B) The observed ratios of green to red from ∼30 bacterial cells from 3 independent fields were determined. The data are presented as the means ± SD (****, P value of <0.0001). The experiment was repeated at least twice. (C) Determination of ROS levels in antibiotic persister cells using the Mrx1-roGFP sensor. Cip or Rif APs of M. smegmatis with the Mrx1-roGFP plasmid were analyzed after 72 h by confocal microscopy. The experiment was performed with two biological replicates, and a representative image is presented. (D) The ratio of blue to green was determined, and the values from individual cells were plotted. The data are presented as the means ± SD (****, P value of <0.0001). (E) The M. smegmatis wild type was treated with Cip and Rif and incubated for 72 h. After incubation, an aliquot was taken, stained with PI and CM-H2DCFDA (ROS indicator), and subjected to confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The fluorescence images were acquired, and a representative image is presented. Viable cells with high ROS levels are indicated with arrowheads.