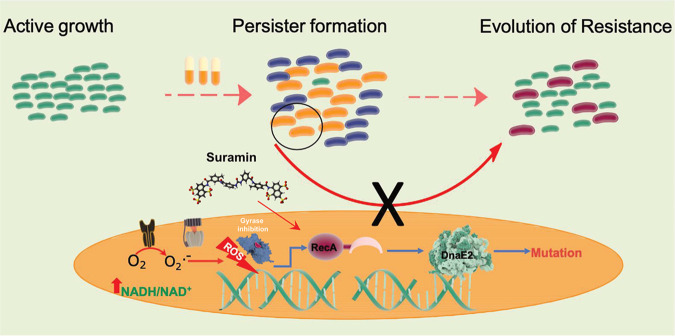
FIG 7.
Mechanism of antibiotic-induced drug resistance in M. smegmatis. A lethal dose kills the majority of the bacteria (blue cells), leaving behind a population of APs (orange cells). The APs display disturbed redox balance leading to the generation of ROS. The high levels of ROS in APs inflict DNA damage, activating RecA and triggering the SOS response, while Cip directly induces the SOS response by causing DNA strand breaks by the inhibition of DNA gyrase. DnaE2, an effector protein of the SOS response, induces mutagenesis, resulting in the emergence of drug resistance (red cells). The presence of suramin, a RecA inhibitor, mitigates antibiotic-induced drug resistance in persisters.