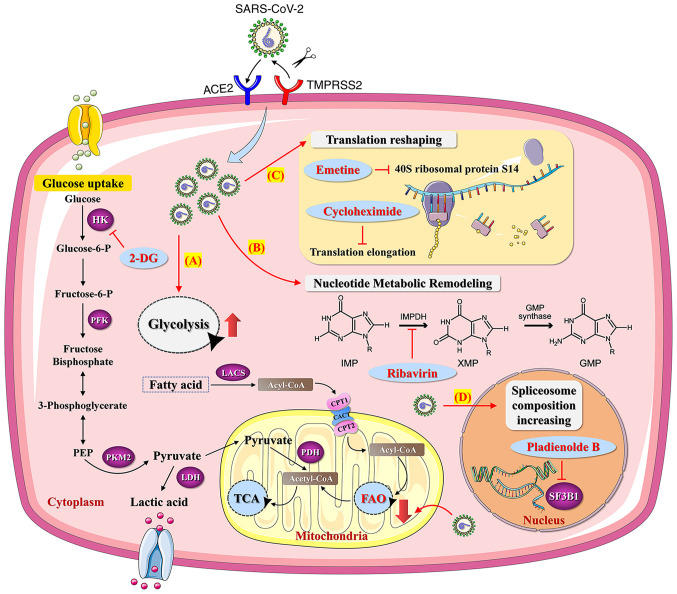
Figure 3.
Effects of SARS-CoV-2 on metabolism pathways of tumor cells and potential metabolic targets for inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 replication in tumor cells. (A) SARS-CoV-2 may increase the rate of tumor productivity by increasing the metabolic ratio of glycolysis/FAO in tumor cells. The application of 2-DG, a hexokinase (rate-limiting enzymes of glycolysis) inhibitor, may suppress the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in tumor cells. (B) SARS-CoV-2 can induce tumor nucleotide metabolic remodeling. The application of Ribavirin may suppress the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in tumor cells. (C) SARS-CoV-2 can induce tumor translation reshaping. The application of Emetine and Cycloheximide may suppress the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in tumor cells. (D) SARS-CoV-2 can increase tumor spliceosome composition. The application of SF3B1 inhibitor may suppress the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in tumor cells. SARS-CoV-2, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; HK, hexokinase; PFK, phosphofructokinase; PKM2, pyruvate kinase isozyme type M2; LDH, lactate dehy- drogenase; LACS, long chain long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase; CPT, carnitine palmitoyltransferase; CACT, carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase; FAO, fatty acid oxidation; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; ACE2, angiotensin converting enzyme 2; TMPRSS2, transmembrane protease serine 2; IMPDH, inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase; IMP, hypoxanthine ribonucleotide; XMP, xanthosine monophosphate; GMP, guanosine 5′-mono- phosphate; 2-DG, 2-Deoxy-D-glucose.