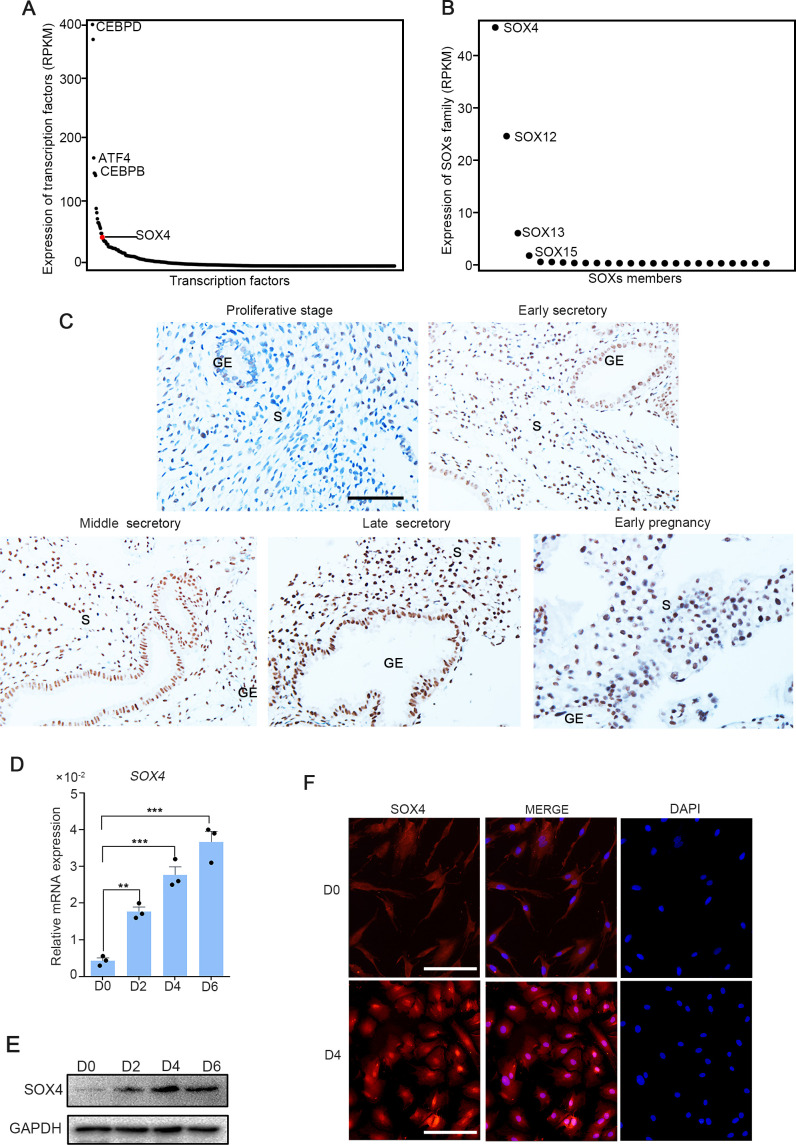
Figure 1. SOX4 is dynamically expressed in human ESCs.
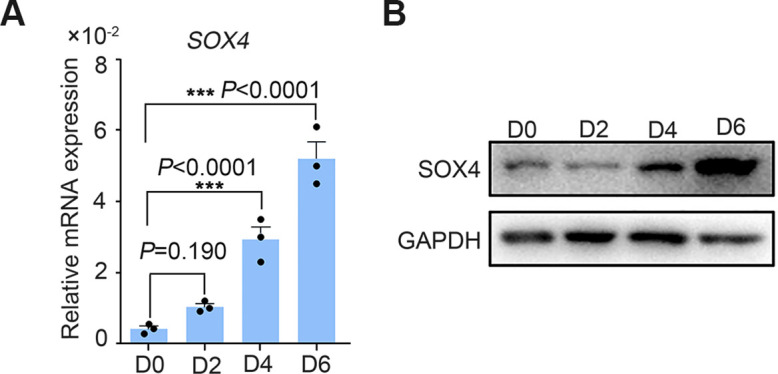
Expression of all transcription factors (A) and SOX family genes (B) in human nondecidualized ESCs by RNA-Seq. The value in Y-axis indicated the RPKM (reads per kilobase per million mapped reads) in RNA-Seq data. (C) Immunohistochemical analysis of endometrial SOX4 protein expression in proliferative, secretory phases (early, middle, and late) of the menstrual cycle and early pregnancy (about 8 weeks). GE: gland epithelium; S: stroma. Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) Expression of SOX4 mRNA levels in decidualized stromal cells at different time points after the E2, MPA, and cAMP treatment. Results are presented as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM); n = 3; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.0001. (E) Expression of SOX4 protein levels in decidualized stromal cells at different time points after the E2, MPA, and cAMP treatment. (F) Immunofluorescent detection of SOX4 protein localization in the undecidualized (D0) and decidualized (D4) human endometrial stromal cells (HESCs). Scale bar: 100 μm.
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Sox family expression in mouse uterine stromal and epithelial cells.
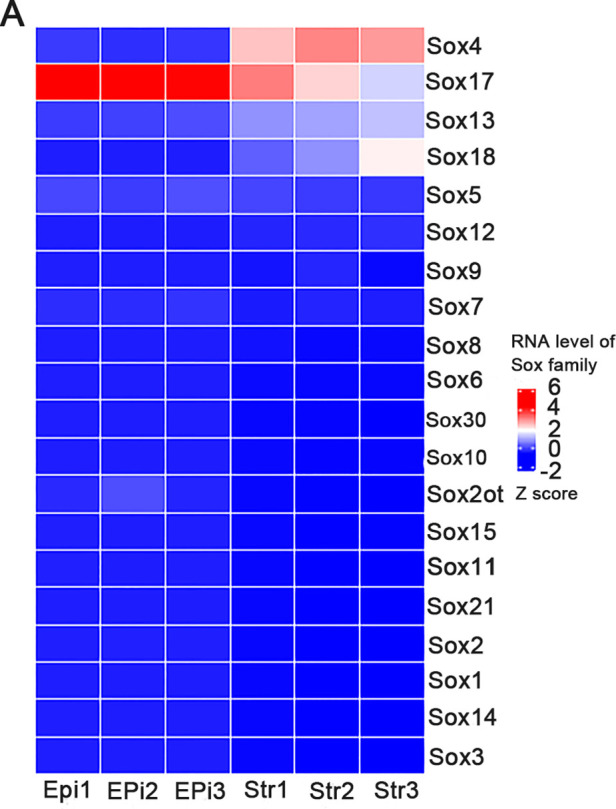
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. SOX4 expression in the primary stromal cell during the decidualization.