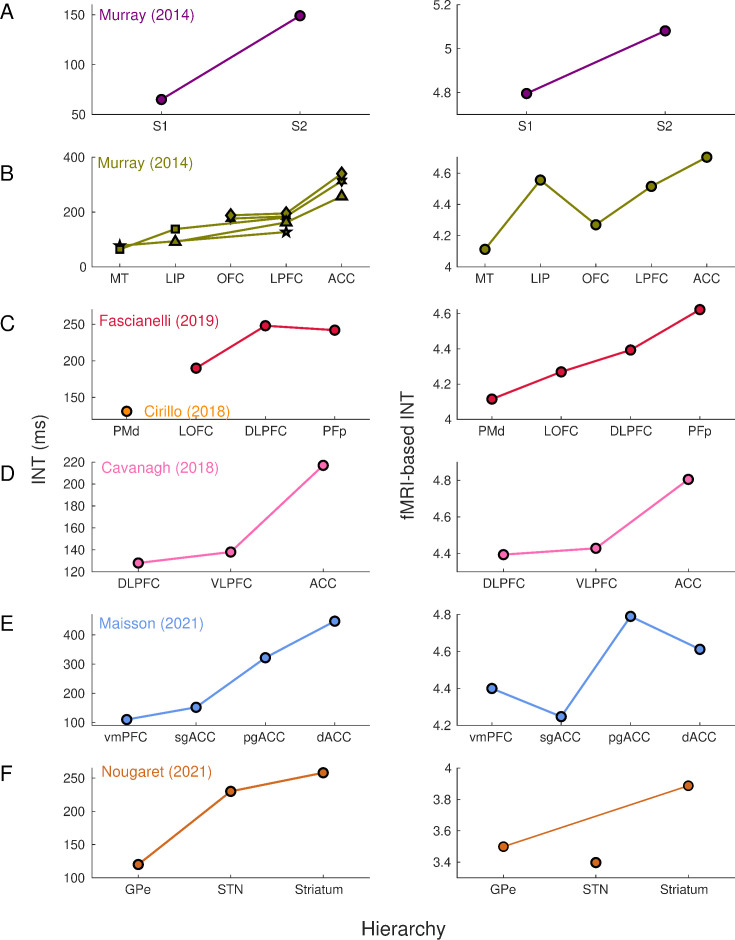
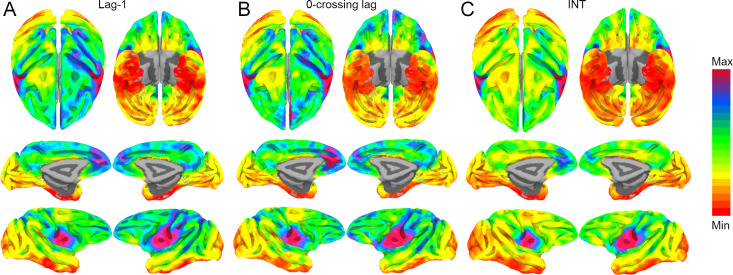
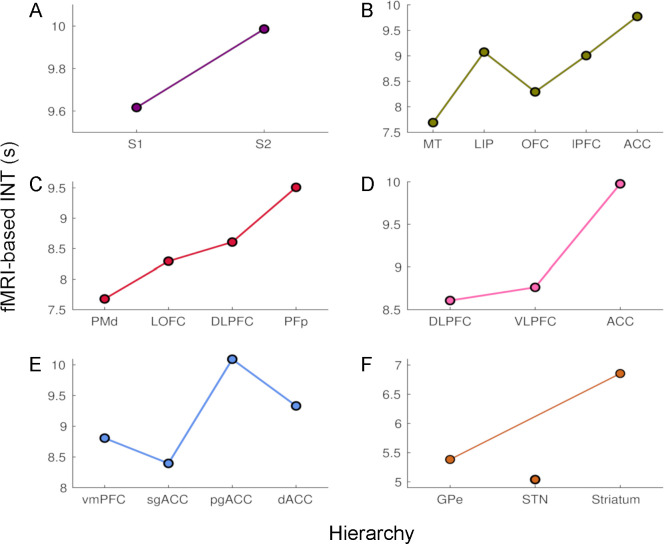
Figure 1. Intrinsic neural timescales estimated from functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electrophysiology reveal a similar hierarchical ordering of cortical and subcortical areas.
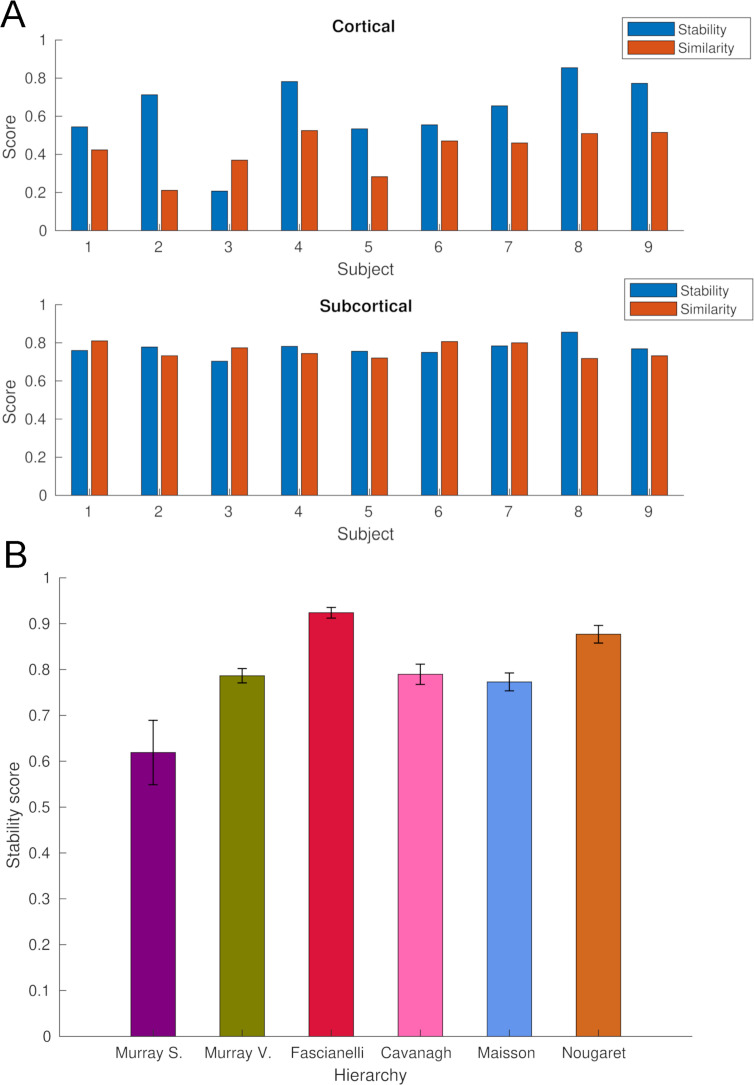
Group-averaged (N=9) INTs were estimated for each area of interest by averaging across voxels. Each color represents a hierarchy estimated from a different electrophysiology data set (Left). The hierarchies estimated from spiking data were replicated via fMRI (Right). Somatosensory (A) and visual (B) hierarchies reported by Murray et al., 2014. Note: Each symbol represents a different data set as originally reported by the respective authors. Frontal hierarchy reported by Fascianelli et al., 2019 and Cirillo et al., 2018 (C). Frontal hierarchy reported by Cavanagh et al., 2016 (D). Medial prefrontal hierarchy reported by Maisson et al., 2021 (E). Subcortical hierarchy reported by Nougaret et al., 2021 (F). The areas were defined bilaterally for each panel to match the recording sites of the data set—the Cortical Hierarchy Atlas of the Rhesus Macaque (Jung et al., 2021) and Subcortical Atlas of the Rhesus Macaque (Hartig et al., 2021) were used when possible (see Supplementary file 1). The hemodynamic INTs were estimated as the sum of the autocorrelation function (ACF) values in the initial positive period—that is, this measurement considers both the number of lags and the magnitude of the ACF values. Hence, the INT does not have a time unit and it is used as a proxy of the timescale of that area, with higher values reflecting longer timescales. See Figure 1—figure supplement 2 for an estimate of the time constant of each area. The INT of individual areas was estimated by taking the average of the voxels’ INT values. The analysis was performed at the group level (N=9). Abbreviations: S1/S2 (primary/secondary somatosensory cortex), MT (middle temporal area), LIP (lateral intraparietal area), OFC (orbitofrontal cortex), LPFC (lateral prefrontal cortex), ACC (anterior cingulate cortex), PMd (dorsal premotor cortex), LOFC (lateral OFC), DLPFC (dorso-lateral PFC), VLPFC (ventro-lateral PFC), PFp (polar prefrontal cortex), vmPFC (ventro-medial PFC), sgACC (subgenual ACC), pgACC (pregenual ACC), dACC (dorsal ACC), GPe (external globus pallidus), STN (subthalamic nucleus). Figure 1—figure supplement 3 depicts single-subject INT stability and similarity and the group-level stability of the INT hierarchies.