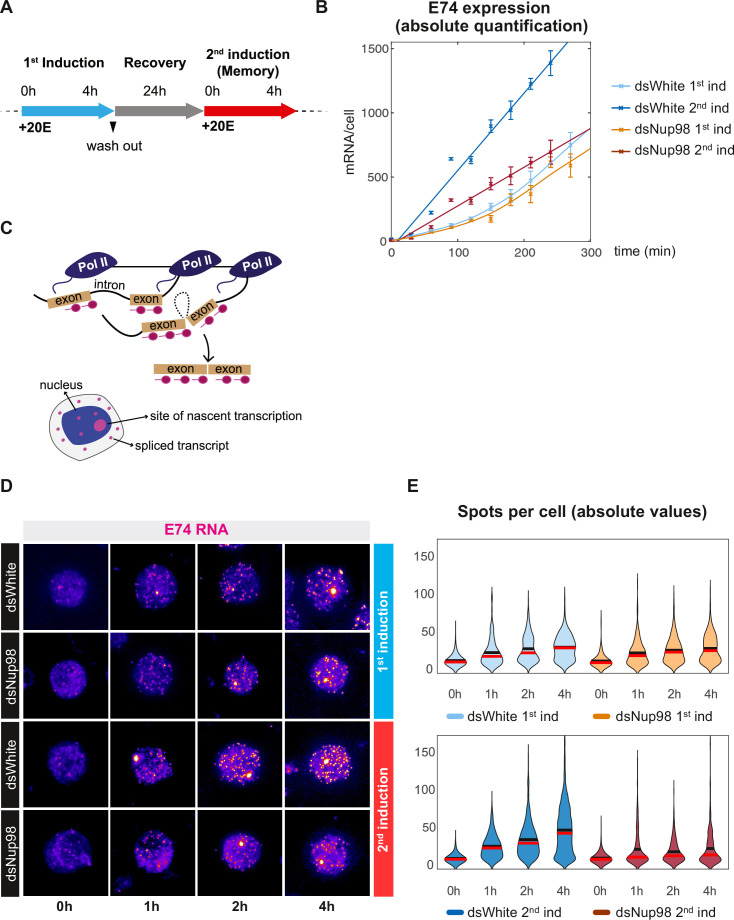
Figure 1. Absolute quantification of E74 induction and transcriptional memory.
(A) Overview of ecdysone/20E treatment. Cells were treated with 5 μM 20E, then washed with fresh media and recovered for 24 hr. Memory response was assessed by incubating cells with 5 μM 20E after recovery period. (B). Absolute number of E74 mRNAs per cell as a function of time after the addition of 20E during either the first or second induction in control (dsWhite) and Nup98 knockdown (dsNup98) S2 cells. Samples were collected every 30 min. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean of three experiments. (C). Schematic of smFISH labeling of sites of nascent transcription and spliced transcripts in either the nucleus or cytoplasm. (D). Representative images of E74 smFISH labeling in single cells during the first and second induction, displayed with the ImageJ ‘red fire’ look-up table. (E). Violin plots of E74 puncta per cell. Mean and median indicated by black and red horizontal lines.