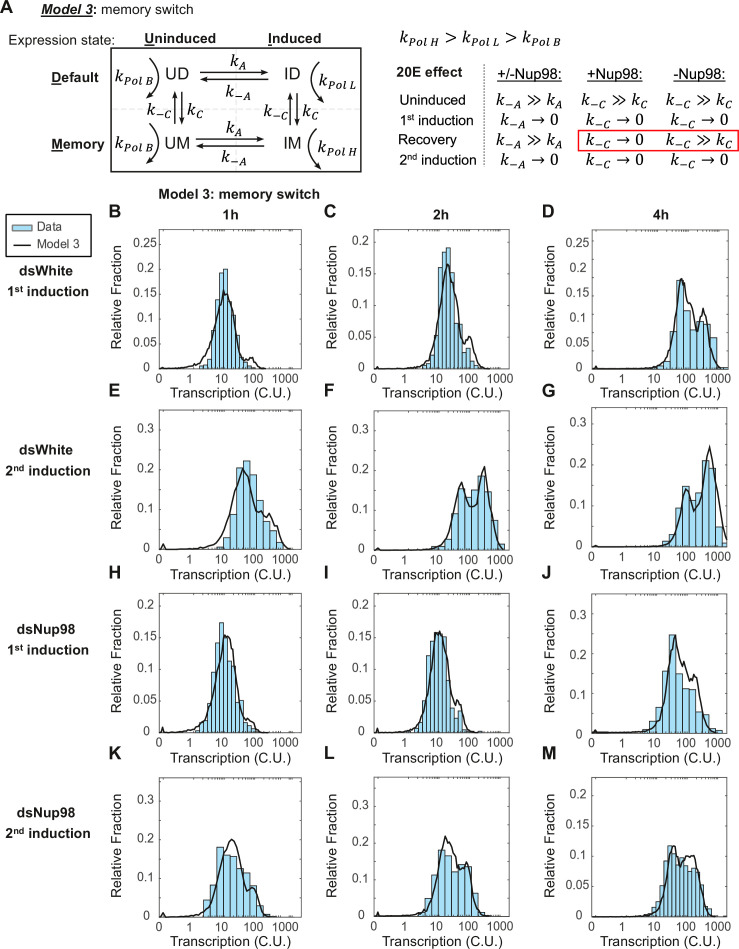
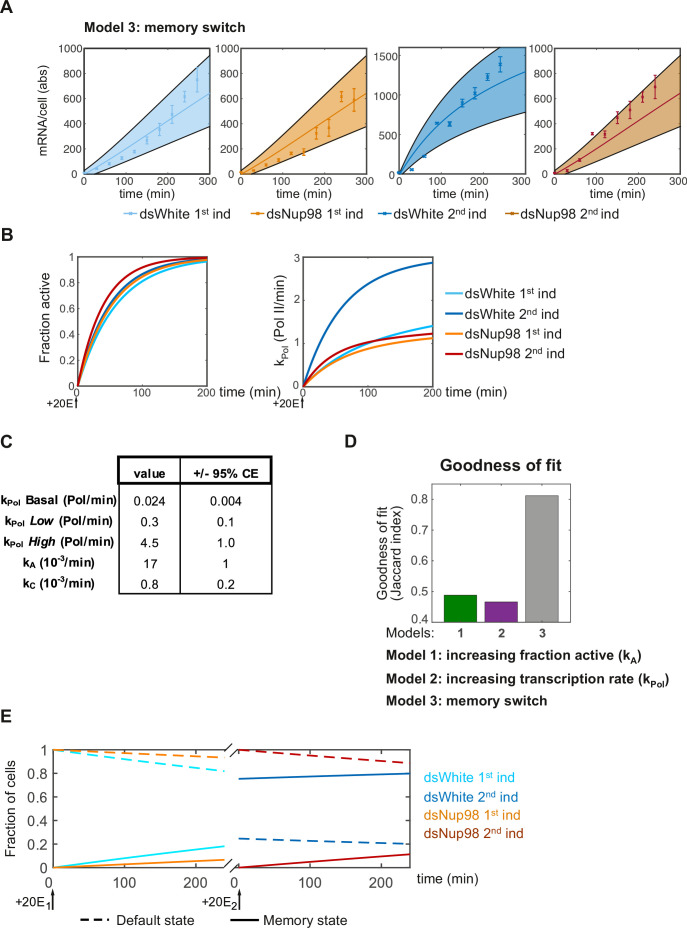
Figure 4. The memory switch model describes the distribution of transcriptional activity.
(A) Promoters can occupy one of four states: Uninduced and Induced (U and I), related to current presence of hormone; and Default and Memory (D and M), associated with prior hormone exposure. The Uninduced state is associated with a basal RNA Pol II rate kPolB, whereas the Induced state shows two independent RNA Pol II rates kPolL and kPolH associated with Default and Memory states, respectively. 20E has two roles: one, to activate transcription by ensuring kA >> k-A, as in earlier models; and two, to increase the rate of conversion from Default to Memory by ensuring kC >> k-C. The role of Nup98 is to maintain kC >> k-C upon withdrawal of 20E. (B–M). Histograms (cyan) show distribution of measured total instantaneous transcriptional activity in normalized units (C.U.), obtained from smFISH of E74 as shown in Figure 1. Lines represent predicted values generated by simulation using best-fitting parameters under the memory switch model.