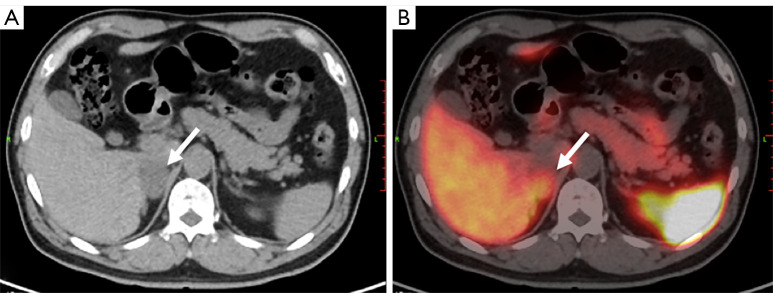
Figure 4.
Adenomatoid tumor of adrenal gland in a 63-year-old male. His pfNMN was 476.3pmol/L, slightly above the normal range, and was defined as borderline. (A) Axial CT image shows a hypointense tumor at the right adrenal gland (arrow). (B) The tumor shows a moderate uptake of 68Ga-DOTA-TATE in the CT and PET fusion image (arrow). The SUVmax was 10.2, SUVR was 0.9, and KS score was 2. This tumor was diagnosed as PCC visually before surgery. Histologic results after surgery indictaed an adenomatoid tumor of the adrenal gland. pfNMN, plasma-free normetanephrine; CT, computed tomography; 68Ga-DOTA-TATE, 68Ga-DOTA(0)-Tyr(3)-octreotate; PET, positron emission tomography; SUVmax, maximal standardized uptake value; SUVR, ratio between the SUVmax of the lesion and the SUVmean of the liver; SUVmean, mean standardized uptake value; KS, Krenning scale; PCC, pheochromocytoma.