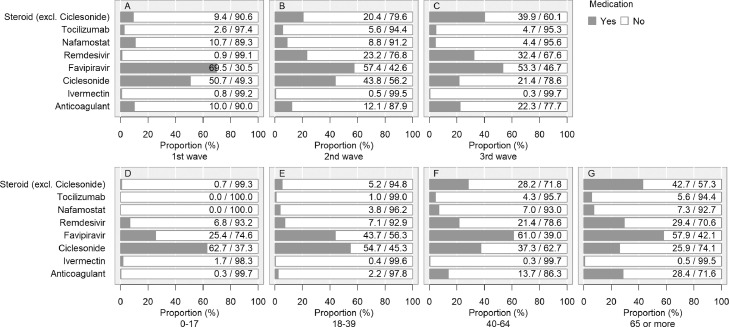
Figure 4.
History of drug administration during hospitalisation.
Medications with antiviral effects against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, immunomodulatory effects against coronavirus disease (COVID-19), and/or immunosuppressive effects against COVID-19 were included. Ciclesonide is available only as an inhalant. Steroids (other than ciclesonide) were administered in 9,450 cases. For oral, intravenous, and inhalation administration, there were 5,279, 5,086, and 86 cases, respectively. There were 9,376 cases of either oral or intravenous administration. If more than one preparation was used for one patient, each was counted. Anticoagulation therapy included unfractionated heparin, low-molecular-weight heparin, fondaparinux, and oral anticoagulants (warfarin and direct oral anticoagulants: dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban) during hospitalisation. In this study, we did not distinguish between prophylactic and therapeutic administration of thromboembolism. We did not count concomitant therapies in the present analysis. The denominator is not the total number of patients, but the number of patients who were administered any drug to treat COVID-19 (n=15,880) for whom the data of each antiviral drug was not missing. For example, the proportion of patients administered favipiravir was calculated as: with favipiravir/(with favipiravir + without favipiravir).