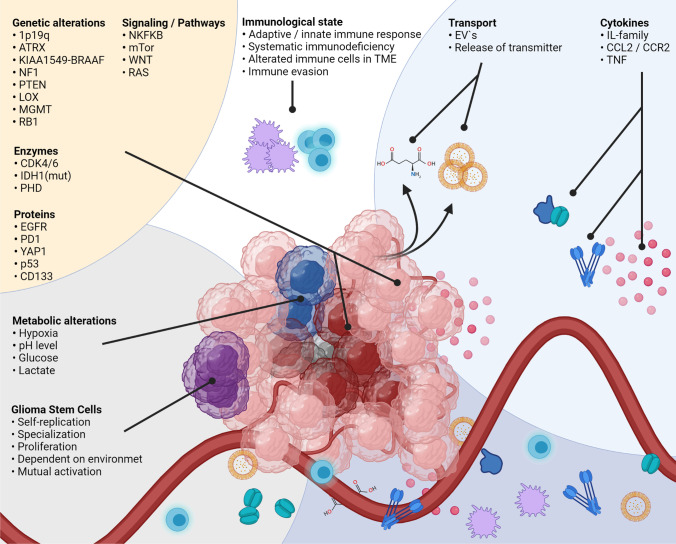
Fig. 4.
The interactions between TME and glioma cells are complex, as the multiple players of widespread origin show. Intracellular factors, pathways, cytokines, genetic alterations, or environmental properties are involved, and the molecular characteristics of glioma cells are dependent on these parameters. Furthermore, vice versa, the glioma molecular patterns influence the TME composition. The detailed interactions are listed in the text. Abbreviations: 1p19q, combined loss of the short-arm chromosome 1 (i.e., 1p) and the long-arm chromosome 19 (i.e., 19q); ATRX, transcriptional regulator ATRX also known as ATP-dependent helicase ATRX (-mut, mutation); BRAF (human gene that encodes a protein called B-Raf); CCL2, CC-chemokine-ligand-2; CCR2, C–C chemokine receptor type 2; CDK4/6, cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6; CD133, CD133–prominin 1, PROM1, is a transmembrane protein; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor (vIII, variant III); EVs, extracellular vesicles; IDH1, isocitrate dehydrogenase-(1) (mut, mutation; wt, wild type); IL-family, interleukin family; KIAA1549-BRAAF, KIAA1549 (protein-coding gene); LOX, lysyl oxidase, also known as protein-lysine 6-oxidase; MGMT, O6-methylguanine–DNA methyltransferase; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; NF1, neurofibromatosis type 1; NF-κB, nuclear factor “kappa-light-chain-enhancer” of activated B-cells; P53, tumor protein P53 or tumor suppressor p53; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; PHD, prolyl hydroxylase domain enzymes; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; RAS, RAS proteins control signaling pathways that are key regulators of normal cell growth and malignant transformation; RB1, RB transcriptional corepressor 1; TME, tumor microenvironment; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; WNT, Wnt signaling pathway; antiporter system xc−