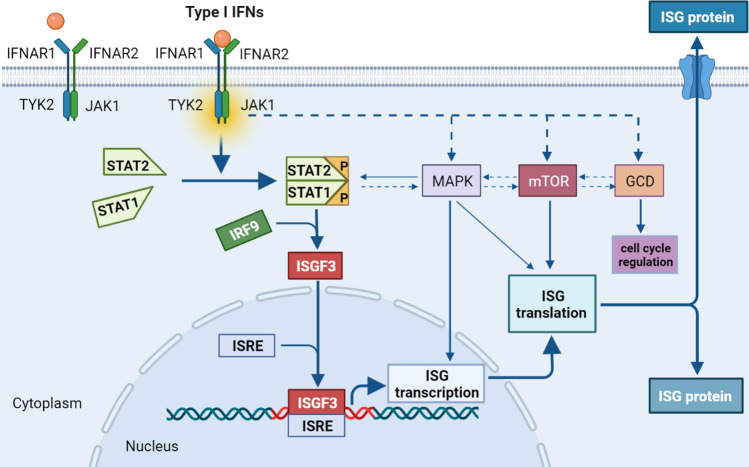
Fig. 1.
Type I IFNs signal transduction pathway. Type I IFNs bind to IFNAR1/IFNAR2 heterodimers to drive the activation of TYK2 and JAK1, which results in the accumulation of activated STAT1 and in the subsequent formation of STAT1–STAT2 heterodimers. Then, the dimerized STATs are combined with IRF9 to form ISGF3, which interacts with ISREs to induce the synthesis of various proteins from ISGs. Meanwhile, “non-classical” pathways, such as the MAPK, mTOR, and GCD pathways, are activated by type I IFNs and trigger the expression of additional ISGs