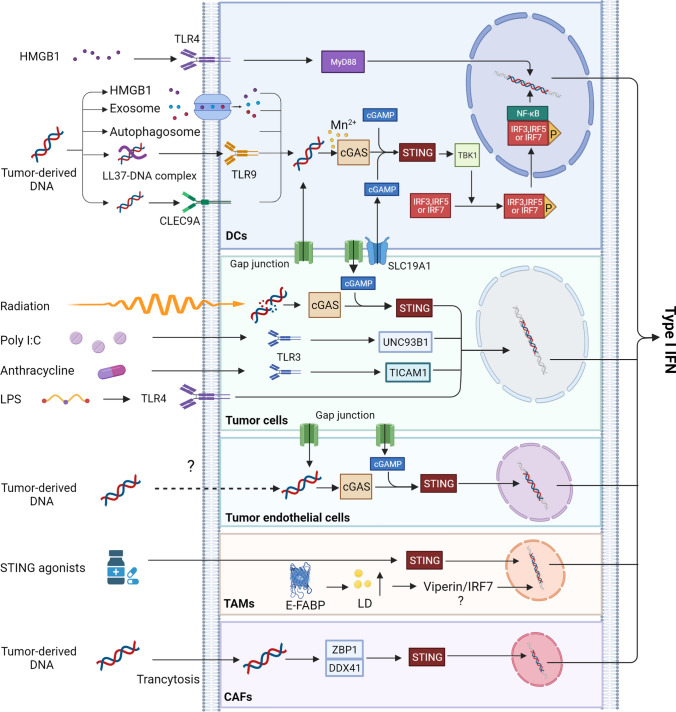
Fig. 2.
The production of type I IFNs in the TME. Tumor-derived HMGB1 induces the production of type I IFNs in DCs via the TLR4-MyD88 pathway. Tumor-derived DNA activates the cGAS/STING pathway to drive the expression of type I IFNs through chaperoning HMGB1, autophagosome, exosome, LL37, or CLEC9A into DCs. And manganese increases dsDNA binding to cGAS. Damaged DNA caused by ionizing radiation (IR) in tumor and endothelial cells triggers cGAS/STING signal to produce type I IFNs. Poly I:C induces overexpressed TLR3 to promote IFN-β production via the UNC93B1 signaling pathway in paclitaxel-resistant colon cancer (HCT-8/PTX) cells. Anthracycline induces the secretion of type I IFNs through the TLR3-TICAM1 pathway in tumor cells. TAMs expressing E-FABPs can produce high levels of IFN-β by upregulating LD. Furthermore, tumor-derived DNA enters into CAFs by transcytosis and is distinguished by ZBP1 and DDX41, then activates STING-IRF3 pathway and induces IFN-β expression